Test: Theoretical Distributions- 5 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation - Test: Theoretical Distributions- 5
The expected value of a constant k is the constant
The probability distribution whose frequency function f(x)= 1/n( x = x1, x2, …, xn) is known as
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The no. of points obtained in a single throw of an unbiased die follow :
The no of points in a single throw of an unbiased die has frequency function
In uniform distribution random variable x assumes n values with
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8 , 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(x = 9) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8 , 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(x = 12) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(x < 15) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8 , 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P 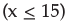 is
is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(x > 15) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(|x – 14| < 5) is
In continuous probability distribution P  means
means
In continuous probability distribution F(x) is called.
The probability density function of a continuous random variable is y = k(x–1), then the value of the constant k is
In continuous probability distribution P(x ≤ t) means
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P( x > 15) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P (x ≤ 15) is
The probability function of a continuous random variable is y = k ( x - 1), (1 ≤ x ≤ 2) then the value of the constant k is
The no of points in a single throw of an unbiased die has frequency function
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P(|x - 14| < 5) is
In a discrete random variable x follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8, 9, 11, 15, 18, 20. Then P( = 9) is
The number of points obtained in a single throw of an unbiased die follows:
In uniform distribution random variable x assumes n values with
Out of 128 families with 4 children each, how many are expected to have at least one boy and one girl?
If the weekly of 5000 workers in a factory follows normal distribution with mean and SD as Rs.700 and Rs.50 respectively, what is the expected number of workers with wages between Rs.660 and Rs.720?
A car hire firm has 2 cars which is hired out everyday. The number of demands per day for a car follows Poisson distribution with mean 1.20. What is the proportion of days on which some demand is refused?(Given e 1.20 = 3.32).
|
114 videos|164 docs|98 tests
|
|
114 videos|164 docs|98 tests
|


















