RRB JE ME CBT 2 Full Test 1 - Railways MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test RRB JE (Railways Junior Engineer) CBT Mock Test Series 2025 - RRB JE ME CBT 2 Full Test 1
In a reversible adiabatic process the ration  is equal to:
is equal to:
 is equal to:
is equal to:| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following engine can be associated with heterogeneous combustion?
A frictionless heat engine can be 100% efficient only if the exhaust temperature is
In an Otto cycle, the heat addition and heat rejection take place at
The rate of heat transfer through a hollow cylinder of inner and outer radii r1 and r2, respectively, depends on
Which of the following quantity is not a property of a system?
In a closed system, a gas undergoes a quasi-equilibrium process as per the law P = (-4V + 10) N.m2 and the volume of the gas, V changes from 1 m3 to 2 m3. The work done will be
Maximum work by an expansion of a gas in a closed system is possible when the process takes place at constant
An ideal air compressor cycle (with clearance) on p-v diagram can be represented by ________ processes.
The rate of radiation of a black body at 0°C is E J/sec. The rate of radiation of this black body at 273°C will be
A Carnot cycle refrigerator operates between 250 K and 300 K. Its coefficient of performance is
A body subjected to coplanar non-concurrent forces will remain in a state of equilibrium if
The maximum frictional force, which comes into play, when a body just begins to slide over the surface of the other body, is known as
The loss of kinetic energy, during inelastic impact of two bodies having masses m1 and m2, which are moving with velocity v1 and v2respectively, is given by
Forces P, 3P, 2P and 5P act along the sides taken in order of a square. The magnitude of the resultant is
A block A is released from the top of smooth inclined plane and slides down the plane. Another block B is dropped from the same point and falls vertically downwards. Which one of the following statements will be true if the friction offered by air is negligible?
Two circular discs have masses in the ratio 1 : 2 and radii in the ratio 2 : 1. The ratio of their moment of inertia about the diameter is
A thin circular ring of mass 100 kg and radius 2 m resting on a smooth surface is subjected to a sudden application of a tangential force of 300 N at a point on its periphery. The angular acceleration of the ring will be
Polar moment of inertia of an equilateral triangle of side ‘x’ is given by
If one of the walls moves in the direction of flow with uniform velocity while the other wall is stationary, then the resulting flow between parallel walls is called ______.
The resultant upward pressure of the fluid on an immersed body is called
Mercury is considered as a superior barometric fluid due to its
The velocity of fluid particle at the centre of the pipe section is:
The concept of stream function which is based on the principle of continuity is applicable to
All the terms of energy in Bernoulli’s equation  have dimension of
have dimension of
A reservoir containing water has two orifices of the same size at depths of 4 m and 9 m below the free surface of water. The ratio of discharges through these orifices is
Shear stress for a general fluid motion is represented by  where n and A are constants. A Newtonian fluid is given by:
where n and A are constants. A Newtonian fluid is given by:






































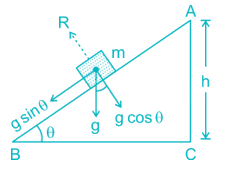

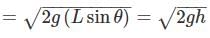
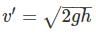


















 it is a case of irrotational flow
it is a case of irrotational flow
 it is a case of steady incompressible irrotational flow
it is a case of steady incompressible irrotational flow
























