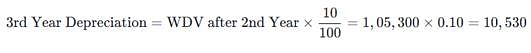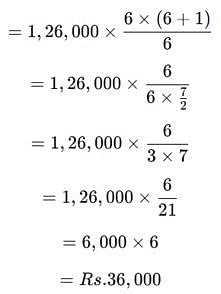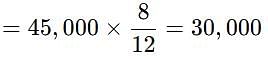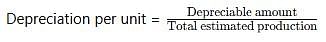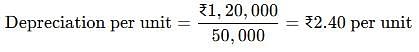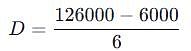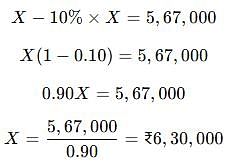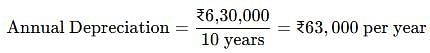Test: Depreciation Accounting - 1 - Commerce MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Accountancy Class 11 - Test: Depreciation Accounting - 1
The portion of the acquisition cost of the asset, yet to be allocated is known as
Which of the following expenses is not included in the acquisition cost of a plant and equipment?
Diminishing method of depreciation provides ______.
Which of the following statements is/are false?
I. The term ‘depreciation’, ‘depletion’ and ‘amortization’ convey the same meaning.
II. Provision for depreciation a/c is debited when provision for depreciation a/c is created.
III. The main purpose of charging the profit and loss a/c with the amount of depreciation is to spread the cost of an asset over its useful life for the purpose of income determination.
Amit Ltd. purchased a machine on 01.01.2003 for Rs. 1,20,000. Installation expenses were Rs 10,000. Residual value after 5 years Rs 5,000. On 01.07.2003, expenses for repairs were incurred to the extent of Rs. 2,000. Depreciation is provided @ 10% p.a. under written down value method. Depreciation for the 4th year = ________.
Original cost = Rs.1,26,000; Salvage value = Nil; Useful life = 6 years. Depreciation for the first year under sum of years digits method will be
Obsolescence of a depreciable asset may be caused by
I. Technological changes.
II. Improvement in production method.
III. Change in market demand for the product or service output.
IV. Legal or other restrictions.
A machine which was bought for $180,000 on 30 April 2008. The residual value was $5,000 and depreciation rate was 25%. Depreciation is to be charged under the reducing balance method on month to month basis. Compute the depreciation at 31st December 2008
Original cost = Rs.1,26,000; Salvage value = Nil; Useful life = 6 years. Depreciation for the first year under sum of years digits method will be
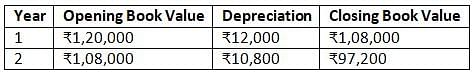
Amit Ltd. purchased a machine on 01.01.2003 for Rs. 1,20,000. Installation expenses were Rs. 10,000. Residual value after 5 years Rs. 5,000. On 01.07.2003, expenses for repairs were incurred to the extent of Rs. 2,000. Depreciation is provided under straight line method.
Annual Depreciation = _____.
Original cost = Rs. 1,26,000. Salvage value = 6,000. Depreciation for 2nd year @ Units of Production Method, if units produced in 2nd year was 5,000 and total estimated production 50,000.
The number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the use of an asset by an enterprise is called as
Which of the following is not true with regard to fixed assets?
Original cost = Rs 1,26,000. Salvage value = 6,000. Useful Life = 6 years. Annual depreciation under SLM =
Original cost = Rs. 1,26,000. Salvage value = 6,000. Depreciation for 2nd year @ 10% p.a. under WDV method =
ABC Ltd. Delhi, paid freight of Rs. 5,000 for bringing one Sortex machine from Mumbai to Delhi which will be used in rice processing. What will be the treatment of freight paid in the books of ABC Ltd.?
In which of the following methods, is the cost of the asset written off in equal proportion, during its useful economic life?
Original Cost = Rs 1,00,000. Life = 5 years. Expected salvage value = Rs. 2,000.
Q. Depreciation for 3rd year as per straight line method is
Company XYZ uses the straight line method of depreciation for all its fixed assets. On 1 January it bought a machine on hire purchase. The cash price was $150,000 and the interest for the year is %16,500. The estimated useful life of the mahine is five years with no residual value. What is the charge for depreciation for the year ended 31 December?
Depreciation under new method for 2002-03 and 2003-04 = _______.
Balance in Machinery A/c on 31.03.2004 = _______.
The balance outstanding to the debit of machinery account as on March 31, 2005 after effecting the above changes was
The balance of the accumulated depreciation account at the end of the year considering the current year’s depreciation charge would be
|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|