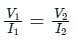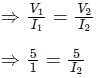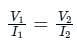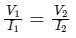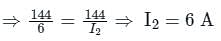Test: Reciprocity Theorem - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Network Theory (Electric Circuits) - Test: Reciprocity Theorem
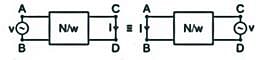
In any bilateral network, if a source of EMF 'E' in any branch produces a current 'I' in any other branch, then the same EMF acting in the second branch would produce the same current 'I' in the first branch. This statement is associated with
What is the current I corresponding to the terminal conditions as shown in the figure below.


| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Reciprocity theorem is applicable to a network
1. Containing R, L and C elements
2. Which is initially not a relaxed system
3. Having both dependent and independent sources
Which of the above is/are correct?
1. Containing R, L and C elements
2. Which is initially not a relaxed system
3. Having both dependent and independent sources
Reciprocity theorem cannot be applied to the circuits having ______.
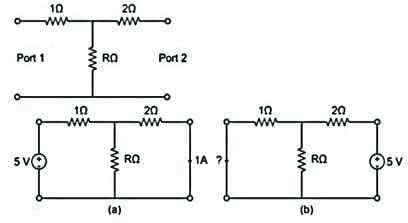
Consider the two-port resistive network shown in the figure. When an excitation of 5 V is applied across Port 1, and Port 2 is shorted, the current through the short circuit at Port 2 is measured to be 1 A (see (a) in the figure).
Now, if an excitation of 5 V is applied across Port 2, and Port 1 is shorted (see (b) in the figure), what is the current through the short circuit at Port 1?
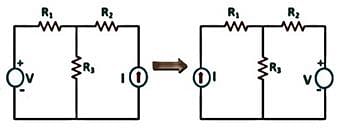
Which of the following step for solution of a network utilizing reciprocity theorem is truly stated?
Which of the following theorem states that the current at one point in a circuit due to a voltage at a second point is the same as the current at the second point due to the same voltage at the first?
Which of the following is the direct method of network analysis?

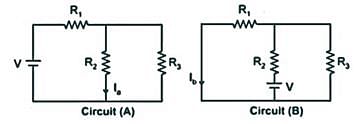
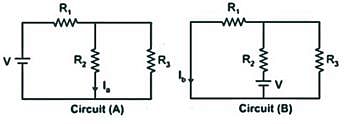
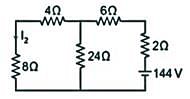
If I1 in the given circuit is 6 A, what will be the current I2 in the following circuit?
In a balanced Wheatstone bridge, if the position of detector and source are interchanged, the bridge will still remain balanced. This inference can be drawn from
|
68 videos|85 docs|62 tests
|
|
68 videos|85 docs|62 tests
|