Test: Respiration in Plants - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Respiration in Plants - 1
The organism which depend on the dead and decaying organic matter is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
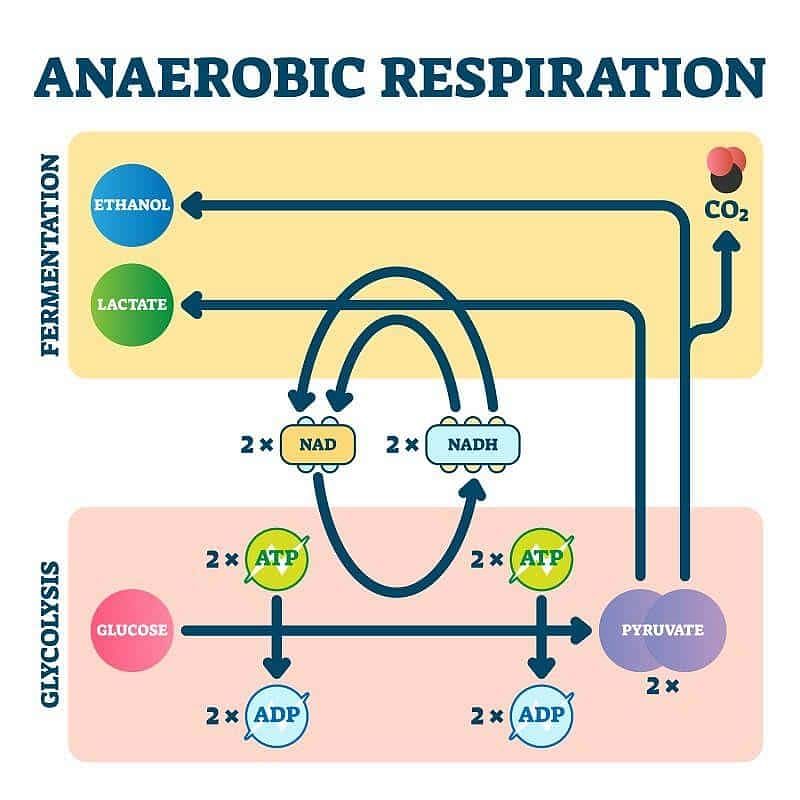
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because:
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is:
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in:
(a) Stomata
(b) Roots
(c) Stems
(d) Lenticels
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.
(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.
(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
Dough kept overnight in warm place becomes soft and spongy due to:
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?
In animal cells, the first stage of glucose break down is:
In kreb cycle, isocitric acid is converted into α-keto glutaric acid by:
When and where anaerobic respiration does occurs in man and yeast?
Krebs cycle is both catabolic and anabolic because it provides
Cytochrome c is the first electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Which of the following statements is false about cytochrome c?
Acetyl CoA forms a 6-C compound after combining with
Which of the following is performed by coenzyme A?
Which one is NOT a preparatory phase or energy spending phase of Glycolysis:
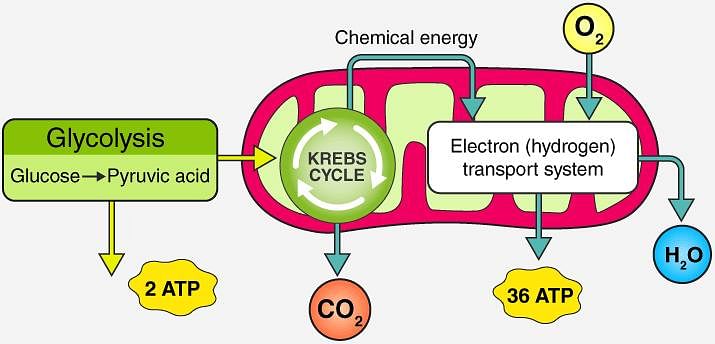
What is the number of ATP molecules that can be regarded as a net gain during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose?
|
181 videos|360 docs|149 tests
|