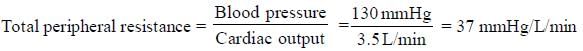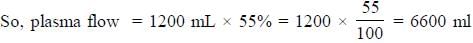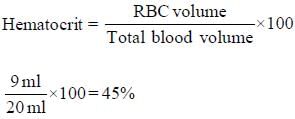Animal Physiology MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2025 - Animal Physiology MCQ
In a chemical synapse, receptors for neurotransmitters are found on
Identify the hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that causes the smooth muscle of the uterus to contract during parturition in mammals
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Choose the combination of statements that are correct for the cerebrum of the human brain
P. It is the largest part of brain
Q. Controls the pituitary hormone secretion
R. Involved in coordinating the movements of the body
S. Receives and processes the sensory information
A class of spermicides (used for contraception) inhibits the flagellar motion of the sperm thereby preventing it from swimming towards the egg. This is achieved by
Which of the following ligament(s) is/are attached to ovary?
P) Ovarian ligaments
Q) Suspensory ligaments R. broad ligaments
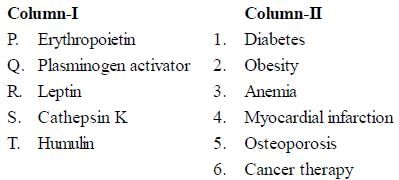
Match the therapeutics in Column-I with their applications in Column-II
Hormones that act on cells near the point of their synthesis and not transported through blood circulation are
A 50 year old man has a mean arterial blood pressure of 130 mmHg, a heart rate of 78 beats/min, a right arterial pressure of 2mmHg and a cardiac output of 3.5 L/min. The total peripheral vascular resistance (mm Hg/L/min) in this man is ______________
In a 35 day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on which day _________.
Cardiac output of the person is 6 lit. and if liver receives 20% of the cardiac output, then the Hepatic plasma flow is ___________(in ml).
In 20 ml sample of whole blood, packed RBC volume is 9 ml. Then the value of hematocrit will be (in %) ___________.