Test: B- Tree - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Question Bank for GATE Computer Science Engineering - Test: B- Tree
Which of the following is the most widely used external memory data structure?
A B-tree of order 4 and of height 3 will have a maximum of _______ keys.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
B-tree and AVL tree have the same worst case time complexity for insertion and deletion.
Figure shown below is B-tree of order 5. What is the result of deleting 130 from the tree?
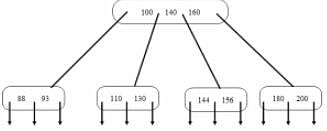
B-tree of order n is a order-n multiway tree in which each non-root node contains __________
Five node splitting operations occurred when an entry is inserted into a B-tree. Then how many nodes are written?
2-3-4 trees are B-trees of order 4. They are an isometric of _____ trees.
What is the best case height of a B-tree of order n and which has k keys?
Compression techniques can be used on the keys to reduce both space and time requirements in a B-tree.
|
63 videos|8 docs|165 tests
|
|
63 videos|8 docs|165 tests
|

















