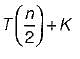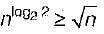Test: Divide & Conquer- 3 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Question Bank for GATE Computer Science Engineering - Test: Divide & Conquer- 3
Which of the following data structures is generally used to implement priority queue?
Following algorithm (s) can be used to sort n integers in the range [1 ... n3] in O(n) time?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The recurrence relation that arises in relation with the complexity of binary search is
For merging two sorted lists of sizes m and n into a sorted list of size m + n, we required comparisons of
Quicksort is run on two inputs shown below to sort in ascending order:
(i) 1 , 2 , 3 .... n .
(ii) n, n - 1, n - 2 , .... 2, 1
Let C1, and C2 be the number of comparisons made for the inputs (i) and (ii) respectively. Then,
Let T(n) be the function defined by T(1) = 1, T(n) 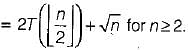 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
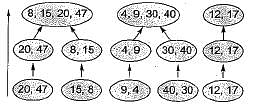
If one uses straight two-way merge sort algorithm to sort the following elements in ascending order:
20,47, 15,8,9,4,40,30, 12, 17
Then the order of these elements after second pass of the algorithm is
|
63 videos|7 docs|165 tests
|
|
63 videos|7 docs|165 tests
|