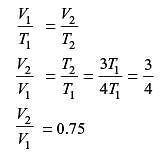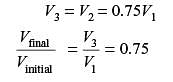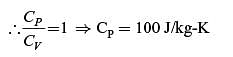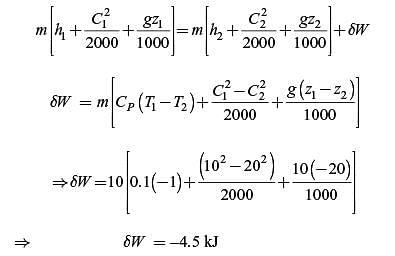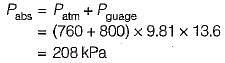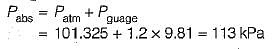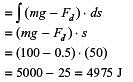Test: Basic Concept - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Thermodynamics - Test: Basic Concept - 3
The study of thermodynamics provides answer to the followings:
1. whether a process is feasible or not
2. to quantity the energy required for a process
3. rate or speed with which a process occurs
4. extent to which a reaction/process takes place
Which of the above statements are correct?
1. whether a process is feasible or not
2. to quantity the energy required for a process
3. rate or speed with which a process occurs
4. extent to which a reaction/process takes place
The volume and temperature of air (assumed to be an ideal gas) in a closed vessel is 2.87 m3 and 300 K, respectively. The gauge pressure indicated by a manometer fitted to the wall of the vessel is 0.5 bar. If the gas constant of air is R = 287 J/kg-K and the atmospheric pressure is 1 bar, the mass of air (in kg) in the vessel is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements:
1. Thermodynamic properties are the macroscopic coordinates significant only for systems existing in states of thermodynamic equilibrium.
2. Engineering thermodynamic studies about transfer and transformation of energy.
3. Engineering thermodynamics studies about storage, transfer and transformation of energy.
Which of the above is/are correct?
2. Engineering thermodynamic studies about transfer and transformation of energy.
3. Engineering thermodynamics studies about storage, transfer and transformation of energy.
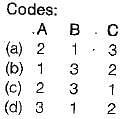
Match the following List-I with List-ll:
List-I
A. Centrifugal fan
B. Control volume
C. Intensive property
D. Microscopic property
List-ll
1. Open system
2. Internal energy
3. Filling a tire at air station
4. Specific energy
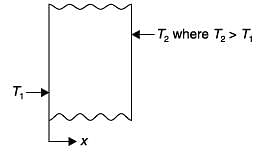
A certain amount of an ideal gas is initially at a pressure p1 and temperature T1. First, it undergoes a constant pressure process 1-2 such that T2 = 3T1/4. Then, it undergoes a constant volume process 2-3 such that T3 = T1/2. The ratio of the final volume to the initial volume of I the ideal gas is
Match the following List-I (Thermometer) with List -II ( Thermometric property)

Work is done on a adiabatic system due to which its velocity changes from 10 m/s to 20 m/s, elevation
increases by 20 m and temperature increases by 1 K. The mass of the system is 10 kg, Cv = 100 J/(kg.K) and gravitational acceleration is 10 m/s2. If there is no change in any other component of the energy of the system, the magnitude of total work done (in kJ) on the system is
Convert the following readings of pressure to kPa, assuming that the barometer reads 760mm of Hg and match the List-I and List-II
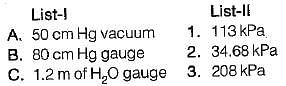
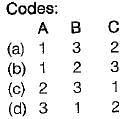
Match the List-I (Terms) with List-ll (Description) and select the correct answer:
List-I
A. Change of state
B. Path
C. Process
List-ll
1. Succession of states
2. One or more properties changes
3. Change of state for specified path
Ice kept in a wail insulated thermo-flask is an example of which system?
For an isolated system executing a process
1. no heat transfer takes place
2. no work is done
3. no mass crosses the boundary
4. no chemical reaction takes place within the system
Which of the above statement are correct?
A body of weight 100 N falls freely a vertical distance of 50 m. The atmospheric drag force is 0.5 N. For the body, the work interaction is
Gauge pressure of air to which the ball must have been originally inflated so that it would equal 1 bar gauge at the stadium is
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|