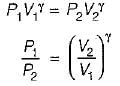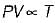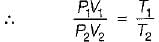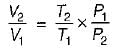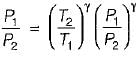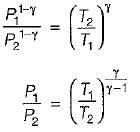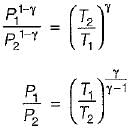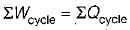Test: Entropy - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Thermodynamics - Test: Entropy - 3
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When a system undergoes a process such that 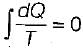 and ΔS > 0, the process is
and ΔS > 0, the process is
A certain amount of fluid at temperature T1 is mixed with an equal amount of the same fluid at temperature T2 in an insulated container with total fluid as the system, consider the following statements
I. Energy of the system is conserved
II. Entropy of the system is conserved
III. Entropy of the system increases
IV. Entropy of the system decreases
Q. Which of the above statements is/are true?
Which one of the following statements applicable to a perfect gas will also be true for an irreversible process
The entropy change for any closed system which undergoes an irreversible adiabatic process
Consider two subsystem 1 and 2 containing same fluid and having same mass m; but at Temperature T1 and T2(T1 > T2) enclosed in an adiabatic enclosure separate by a partition, if the partition is removed and the fluids are allowed to mix. The entropy change of process is
For the isentropic expansion of an ideal gas from the initial conditions P1,T1 to the final conditions P2,T2, which one of the following relations is valid?
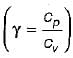
The change in entropy of the system, ΔSsys, undergoing a cyclic irreversible process is
In a reversible isothermal process, an ideal gas expands to four times its initial volume. The change in entropy is
High pressure steam is expanded adiabatically and reversible through a well insulated turbine which produces some shaft work. If the enthalpy change and entropy change across the turbine are represented by ΔH and ΔS, respectively, for this process:
A system undergo a state change from 1 to 2, according to second law of thermodynamics for the process to be feasible, the entropy change (S2 - S1) of the system
The following four figure have been drawn to represent a fictitious thermodynamic cycle, on P - V and T - S planes
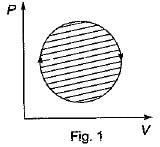
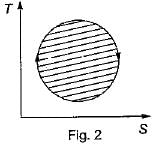
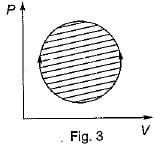
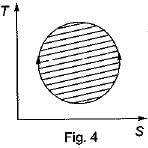
According to first Saw of thermodynamics, equal areas are enclosed by
Four process of thermodynamic cycle are shown in figure on P-V diagram in the sequence 1 -2-3-4. The corresponding correct sequence of these process in the T-S plane shown in figure will be
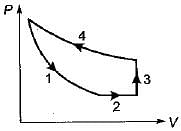
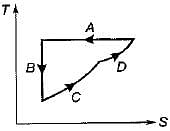
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|


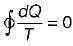 Cycle is reversible
Cycle is reversible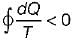 Cycle is irreversible
Cycle is irreversible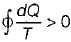 Cycle is impossible
Cycle is impossible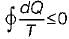 For cycle is possible
For cycle is possible