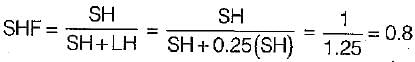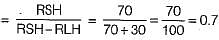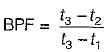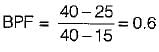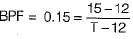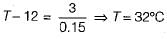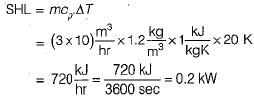Test: Psychrometric Chart & Its Application to Air-Conditioning - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Thermodynamics - Test: Psychrometric Chart & Its Application to Air-Conditioning - 3
In an air-conditioning plant the refrigeration load on the coil is 100 TR. The mass and enthalpy of air leaving the coil are 420 kg/minute and 40 kJ/kg respectively. What will be the enthalpy of the air at the inlet to the coil under these conditions.
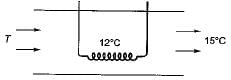
Water in an insulative evaporative cooler evaporates at the rate of 0.003 kg/s. Air flow rate is 1 kg/s. What is the air temperature decrease if the specific heat of humid air is 1 kJ/kg K and latent heat of water is 2500 kJ/kg?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Milk Chilling plant
B. Textile Mills
C. Biological process industry
List-ll
1. Strict control of temperature and humidity
2. Strict control of humidity
3. Strict control of temperature
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3
(c) 2 3 1
(d) 2 1 3
List-I
A. Milk Chilling plant
B. Textile Mills
C. Biological process industry
List-ll
1. Strict control of temperature and humidity
2. Strict control of humidity
3. Strict control of temperature
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3
(c) 2 3 1
(d) 2 1 3
In a counter flow cooling tower, warm water enters at temperature of Tw. The dry bulb and wet bulb temperatures of air entering the tower are TDBT and TWBT respectively. The maximum temperature of water at the exit of the cooling tower is
The latent heat load in an auditorium is 25% of the sensible heat load. The value of sensible heat factor (SHF) is equal to
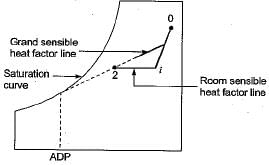
Room sensible heat factor will be equal to, if room sensible heat and room latent heat are equal to 70 kW and 30 kW respectively
Which of the following properties increase(s) during sensible heating of air-water vapour mixture?
1. Relative humidity
2. Humidity ratio
3. Wet bulb temperature
4. Specific enthalpy of air-vapour mixture
Q. Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Atmospheric air at DBT of 15°C enters a heating coil whose surface temperature is maintained at 40°C. The air leaves the heating coil at 25°C. What will be the by-pass factor of heating coil?
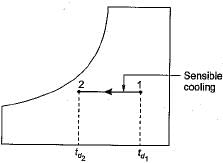
In the case of a cooling coil with non-zero by pass factor, the apparatus dew point temperature lies at the intersection point of
If moist air is sensibly cooled above its dew point which of the following statements are correct:
1. Relative humidity decreases
2. Wet bulb temperature decreases
3. Wet bulb temperature increases
4. Humidity ratio remains constant
Q. Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Air (at atmospheric pressure) at a dry bulb temperature of 40°C and wet bulb temperature of 20°G is humidified in an air washer operating with continuous water recirculation. The wet bulb depression (i.e. The difference between the dry bulb and wet bulb temperatures) at the exit is 25% of that at the inlet. The dry bulb temperature at the exit of the air washer is . closest to
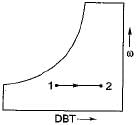
Which one of the following is correct for the process 1-2 shown below
The supply air temperature is 15°C and apparatus dew point is 12°C for the coding coil with by pass factor of 0.15. What is the temperature at inlet of cooling coil
Various psychrometric processes are shown in the figure below:

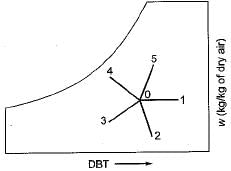
The matching pair are
The following statements are concerned with psychrometric chart:
1. Constant relative humidity lines are uphill straight lines to the right
2. Constant wet bulb temperature lines are downhill straight lines to the right
3. Constant specific volume lines are downhill straight lines to the right
4. Constant enthalpy fines are coincident with constant wet bulb temperature lines
Q. Which of the statements are correct?
Water at 42°C is sprayed into a stream of air at atmospheric pressure, dry bulb temperature of 40°C and a wet bulb temperature of 20°C. The air leaving the spray humidifier is not saturated.
Q. Which of the following statements is true?
For air at a given temperature, as the relative humidity is increased isothermally,
An air-conditioned room of volume 10 m3 has infiltration of air equivalent of 3 air changes. Density of air is 1.2 kg/m3, specific heat Cp is 1 kJ/kg-K and temperature difference between room and ambient air is 20 K. The sensible heat load due to infiltrated air is
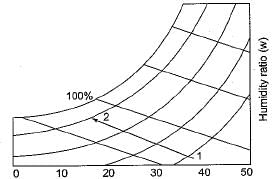
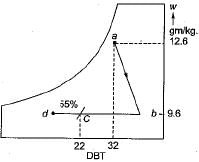
A classroom is to be air-conditioned by obtaining the comfort conditions of 22°C DBT ad 55% RH from outdoor conditions of 32°C DBT and 22°C WBT. The weight of outside air supplied is 30 kg/min. The comfort conditions required are achieved first by chemical dehumidification and then by cooling with a cooling coil as shown in the psychrometric chart below. What is the capacity of the dehumidification in kg/hr?
For an office building the outdoor design conditions are 45°C dbt and humidity ratio of 0.015. The indoor design conditions are 25°C dbt and 0.01 humidity ratio. The supply air state is 15°C dbt and 0.007 humidity ratio. If the supply air flow rate is 1000 m3/min and fresh air flow rate is 100 m3/min, room sensible and room latent heat loads are, respectively
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|