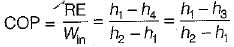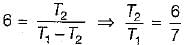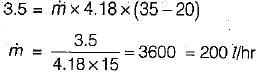Test: Refrigeration Cycles & Systems - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Thermodynamics - Test: Refrigeration Cycles & Systems - 3
The flash chamber in a single stage simple vapour compression cycle serves to
In a hermetically seated compressor unit,
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a domestic refrigerator, periodic defrosting is required because frosting
Pressure drop due to ‘wire drawing' in actual vapour compression cycle is observed at
Large sized industrial air-conditioning plant are
The COP of a Carnot refrigeration cycle decreases on
COP of a domestic refrigerator in comparison to domestic air conditioner will be
The correct sequence of Vapour Compression (VC), Vapour Absorption (VA) and Steam Injection (SE) refrigeration cycles in increasing order of the COP is
In steam-injection system compression is achieved by
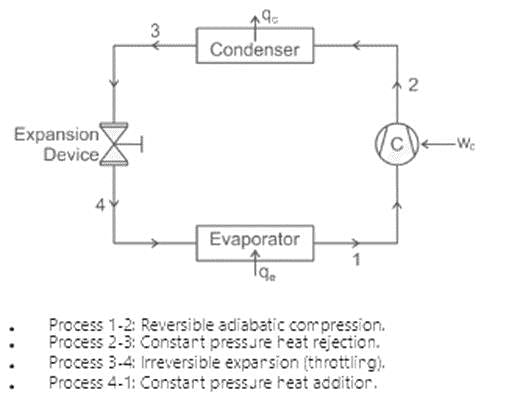
Which one of the following sequence is correct in vapour compression cycle
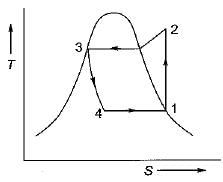
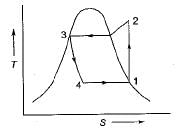
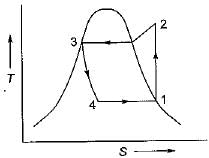
In a vapour-compression refrigeration cycle, if h1 and h2 denote the enthalpies at inlet and exit of the compressor respectively, h3 is the enthalpy at the exit of the condenser and h4 is the enthalpy at the inlet of the evaporator, then COP for the cycle is
Formation of frost on evaporator of refrigerator
In a vapour compression cycle, the refrigerant immediately after expansion valve is
Sub-cooling in a refrigeration cycle have effect of
The effects of superheating of vapour in the evaporator and sub-cooling of condensate in the condenser:
Flash chamber is used in refrigeration for which one of the following?
The thermodynamic cycle used in aircraft refrigeration is
In aircraft, air refrigeration cycle is used because of
In an aircraft refrigeration system, pressure at the cooling turbine outlet is equal to
Which of the following machines can be used to obtain refrigeration at the place where there is no electric power?
In the absorption refrigeration cycle, the compressor of the vapour compression refrigeration cycle is replaced by
Where in an oil separator in vapour compression refrigeration system installed?
Match List-I (Effect) with List-ll (Process) in the case of an ideal refrigeration cycle and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Work input
B. Heat rejection
C. Expansion
D. Heat absorption
List-ll
1. Constant pressure at higher temperature
2. Isentropic compression
3. Constant temperature at lower pressure
4. Isenthalpic process
Codes: A B C D
(a) 4 1 2 3
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 2 1 4 3
(d) 4 2 3 1
A Carnot refrigerator has a COP of 6. What is the ratio of the lower to the higher absolute temperature
A one ton capacity water cooler cools water steadily from 35°C to 20°C. The specific heat of water is 4.18 kJ/kgK. The water flow rate will be nearly
In every real refrigeration cycle, ratio of heat absorbed to heat rejected is
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|
|
29 videos|65 docs|36 tests
|