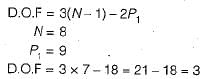Test: Simple Mechanisms - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Simple Mechanisms - 3
In a Kinematic chain, a quarternary joint is equivalent to
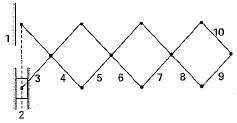
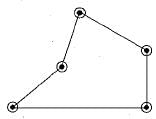
The Kinematic planar chain shown in the given figure is a

The number of degree of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joint is
The method of obtaining different mechanism by fixing different links of a kinematic chain is known as
The Grubler’s criteria for planar mechanism is given by f = 3(n-1) - 2j
j in the equation is
The following is the inversion of the slider-crank mechanism
A. Whitworth quick return mechanism
B. Hand pump
C. Oscillating cylinder engine
Which one of the following mechanism represents an inversion of the single slider crank chain
For a 4-bar linkage in toggle position, the value of mechanical advantage is
The number of degrees of freedom of a five link planer mechanism with five revolute pairs as shown in the figure is
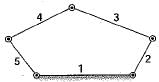
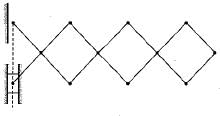
How many degree of freedom does the kinematic chain as shown in figure below have, when it undergoes planer motion.
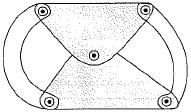
Which one of the following statements is correct?
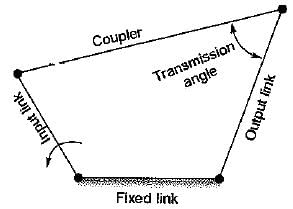
Transmission angle is the angle between
The length of the links of a 4-bar linkage with revolute pairs only are p, q, r and s units. Given that p < q < r< s. Which of these iinks should be the fixed one, for obtaining a ‘double crank’ mechanism?
In a four-bar linkage, the sum of the lengths of the smallest and the longest link is less than the sum of the lengths of the other two links. If the smallest link is fixed, the linkage becomes a
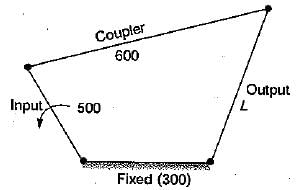
The input link, coupler link and the fixed link of a four bar mechanism have lengths 500 mm, 600 mm and 300 mm, respectively. When the input link is rotated by a motor, the output link can make complete revolutions if its length ‘L in mm satisfied the condition
Match the items in columns I and II.
Column-I
P. Higher kinematic pair
Q. Lower kinematic pair
R. Quick return mechanism
S. Mobility of a linkage
Column-ll
1. Grubler’s equation
2. Line contact
3. Euler's equation
4. Planer
5. Shaper
6. Surface contact
A point on a connecting link of a double slider crank mechanism traces a
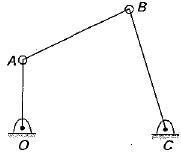
The four bar mechanism shown in the figure (Given : OA = 3 cm, AB = 5 cm, BC = 6 cm, OC = 7 cm) is a
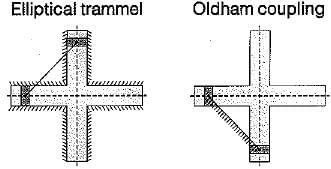
The double slider-crank chain is shown below in the diagram in its three possible inversions. The link shown hatched is the fixed link:
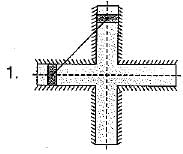
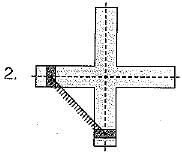
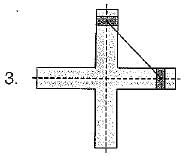
Q. Which one of the following statements is correct?
A planer mechanism has 8 links and 10 rotary joints. The number of degrees of freedom of the mechanism, using Grubler's criterion, is
For a mechanism shown below, the mechanical advantage for the given configuration is

Match the following:
(Type of Mechanism)
P. Scott-Russel mechanism
Q. Geneva mechanism
R. Offset slider-crank mechanism
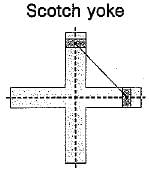
S. Scotch Yoke mechanism
(Motion Achieved)
1. Intermittent motion
2. Quick return motion
3. Simple harmonic motion
4. Straight line motion
Match List-I with List-lI and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Pantograph
B. Single slider crank chain
C. Double slider crank chain
D. Straight line motion
List-II
1. Scotch yoke mechanism
2. Double lever mechanism
3. Tchebicheff mechanism
4. Double crank mechanism
5. Hand pump
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 4 3 5 1
(b) 2 5 1 3
(c) 2 1 5 3
(d) 4 5 2 1