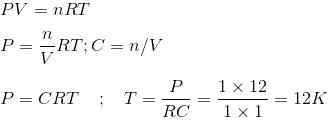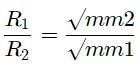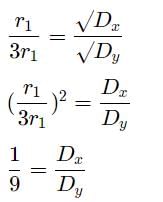R.C. Mukherjee Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - R.C. Mukherjee Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT)
At constant temperature, in a given mass of an ideal gas -
Three flasks of equal volumes contain CH4, CO2 and Cl2 gases respectively. They will contain equal number of molecules if -
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 2 litres at STP. Keeping the pressure constant at what temperature would the gas occupy a volume of 4 litres -
If 500 ml of a gas 'A' at 1000 torr and 1000 ml of gas B at 800 torr are placed in a 2L container, the final pressure will be-
Two flasks A and B of 500 ml each are respectively filled with O2 and SO2 at 300 K and 1 atm. pressure. The flasks will contain-
In the gas equation PV = nRT, the value of universal gas constant would depend only on -
A 0.5 dm3 flask contains gas 'A' and 1 dm3 flask contains gas 'B' at the same temperature. If density of A = 3.0 gm dm-3 and that of B = 1.5 gm dm-3 and the molar mass of A = 1/2 of B, then the ratio of pressure exerted by gases is-
When the pressure of 5L of N2 is doubled and its temperature is raised from 300K to 600K, the final volume of the gas would be-
If the pressure of a gas contained in a closed vessel in increased by 0.4% when heated by 1°C its initial temperature must be :
A thin ballon filled with air at 47°C has a volume of 3 litre. If on placing it in a cooled room its volume becomes 2.7 litre, the temperature of room is :
If a mixture containing 3 moles of hydrogen and 1 mole of nitrogen is converted completely into ammonia, the ratio of initial and final volume under the same temperature and pressure would be:
SO2 at STP contained in a flask was repleced by O2 under identical conditions of pressure, temperature and volume. Then the weight of O2 will be ______ SO2.
Assuming that O2 molecule is spherical in shape with radius 2Å, the percentage of the volume of O2 molecules to the total volume of gas at S.T.P. is :
Two flasks of equal volume are connected by a narrow tube (of negligible volume) all at 27°C and contain 0.70 mole of H2 at 0.5 atm. One of the flask is then immersed into a bath kept at 127°C, while the other remains at 27°C. The final pressure in each flask is :
Two flasks of equal volume are connected by a narrow tube (of negligible volume) all at 27°C and contain 0.70 moles of H2 at 0.5 atm. One of the flask is then immersed into a bath kept at 127° C, while the other remains at 27°C . The number of moles of H2 in flask 1 and flask 2 are:
A gas is heated from 0°C to 100°C at 0.1 atm pressure .If the initial volume of the gas is 10.0 l, its final volume would be :
Under what conditions will a pure sample of an ideal gas not only exhibit a pressure of 1 atm but also a concentration of 1 mol litre-1. [R = 0.0892 litre atm mol-1 K-1]
A and B are two identical vessels. A contains 15 g ethane at 1atm and 298K. The vessel B contains 75 g of a gas X2 at same temperature and pressure. The vapour density of X2 is :
The density of neon will be highest at :
A 0.5 dm3 flask contains gas A and 1 dm3 flask contains gas B at the same temperature. If density of A = 3 g/dm3 and that of B = 1.5 g/dm3 and the molar mass of A = 1/2 of B, the ratio of pressure exerted by gases is :
A cylinder is filled with a gaseous mixture containing equal masses of CO and N2. The partial pressure ratio is:
A gas X diffuses three times faster than another gas Y the ratio of their densities i.e., Dx : Dy is-
At STP, a container has 1 mole of Ar, 2 moles of CO2, 3 moles of O2 and 4 moles of N2. Without changing the total pressure if one mole of O2 is removed, the partial pressure of O2 :
Equal weights of ethane & hydrogen are mixed in an empty container at 25°C, the fraction of the total pressure exerted by hydrogen is :
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of hydrogen. Partical presure of hydrogen will be :
A compound exists in the gaseous phase both as monomer (A) and dimer (A2). The atomic mass of A is 48 and molecular mass of A2 is 96. ln an experiment 96 g of the compound was confined in a vessel of volume 33.6 litre and heated to 237°C. The pressure developed if the compound exists as dimer to the extent of 50% by weight under these conditions will be :
Three footballs are respectively filled with nitrogen, hydrogen and helium. If the leaking of the gas occurs with time from the filling hole, then the ratio of the rate of leaking of gases () from three footballs (in equal time interval) is :
The rates of diffusion of SO3, CO2, PCl3 and SO2 are in the following order-
20 ℓ of SO2, diffuses through a porous partition in 60 seconds. Volume of O2 diffuse under similar conditions in 30 seconds will be :
See the figure :
The valves of X and Y opened simultaneously. The white fumes of NH4Cl will first form at :
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|