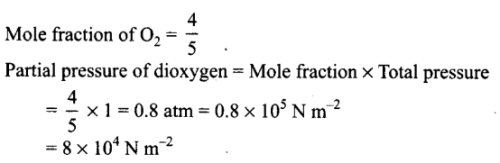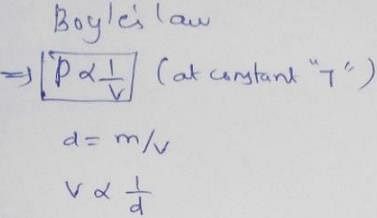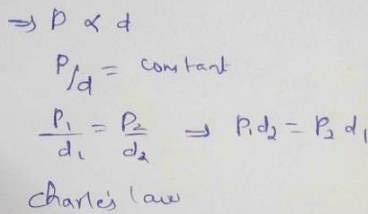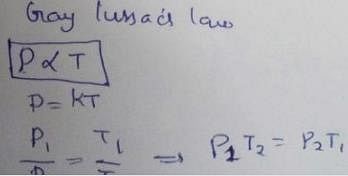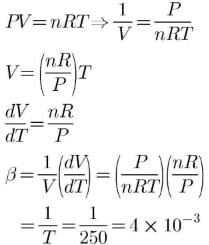Test: Boyle's & Charles Law (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Boyle's & Charles Law (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-4) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. A sample of an ideal gas occupies 20 L under a pressure of 0.5 atm and under isothermal condition. On increasing its pressure to 1.0 atm, its volume will be
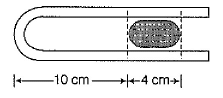
A 10.0 cm column of air is trapped by a column of Hg 4.00 cm long in a capillary tube of uniform bore when the tube is held horizontally at 1 atm. Length of the air column when the tube is held vertically with the open end up is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Volume of an ideal gas is to be decreased by 10% by increase of pressure by x% under isothermal condition. Thus, x is
Density of an ideal gas at 298 K and 1.0 atm is found to be 1.25 kg m-3. Density of the gas at 1.5 atm and at 298 K is
Direction (Q. Nos. 5-9) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. An ideal gas is at 300 K and 1 atm. Then volume remains constant if
The pressure of a 1:4 mixture of dihydrogen and dioxygen enclosed in a vessel is one atmosphere. What would be the partial pressure of dioxygen?
Select correct matching of laws with their corresponding relations.
Consider gases confined by a liquid, as shown in figure.
Density of the liquid = d (all values in SI unit)
Then
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-11) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
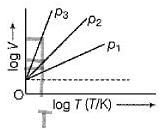
For Charles’ law, graphical representation between log V and log T under isobaric condition is shown below for equation V = kT.
Q. Relation between p1, p2 and p3 is
For Charles’ law, graphical representation between log V and log T under isobaric condition is shown below for equation V = kT
Q. Volume V = constant k, when
Direction (Q. Nos. 12) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q.
Graphicaily Boyle’s law can be represented by various options depending on coordinates. Match the graphs in Column t with their coordinates in Column II and select the correct alternate from the codes given beiow.
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Isothermally compressibility of an ideal gas is
Q.
What is the value of a at 0.2 bar?
Cubic expansion coefficient (β) for an ideal gas is
Q.
Its value at 250 K is x * 10-3 K -1. What is value of x?
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|