JEE Exam > JEE Tests > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - JEE MCQ
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - JEE MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties for JEE 2024 is part of Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced preparation. The Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties questions and answers have been
prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties below.
Solutions of Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE & Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 1
Elements of which of the following group(s) of periodic table do not form hydrides?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 1
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 2
Which of the following statement is true regarding the order of reactivity of halogens?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 3
What is the temperature required in presence of molybdenum and iron for nitrogen to combine with hydrogen?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 4
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 5
The alkali metals form salt-like hydrides by the direct synthesis at elevated temperature. What is the correct order of thermal stability of these hydrides ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 5
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 6
Which of the following chemicals is not present in clear hard water?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 7
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 8
Hard water is not fit for washing clothes because
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 8
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 9
Which of the following statements do not define the characteristic property of water "Water is a universal solvent"
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 9
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 10
Chemical A is used for water softening to remove temporary hardness. A reacts with sodium carbonate to generate caustic soda. When 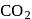 is bubbled through a solution of A, it turns cloudy. What is the chemical formula of A?
is bubbled through a solution of A, it turns cloudy. What is the chemical formula of A?
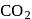 is bubbled through a solution of A, it turns cloudy. What is the chemical formula of A?
is bubbled through a solution of A, it turns cloudy. What is the chemical formula of A?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 10
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 11
What is a result of the reaction of heavy water with sodium?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 11
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 12
The following methods can not be used to remove permanent hardness of water
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 13
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 14
What is formed when calcium carbide reacts with heavy water?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 14
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 15
The dielectric constant of  is
is  The electrostatic force of attraction between
The electrostatic force of attraction between  and
and  will be
will be
 is
is  The electrostatic force of attraction between
The electrostatic force of attraction between  and
and  will be
will be
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 15
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 16
Observe the following statements
1. Heavy water is harmful for the growth of animals.
2. Heavy water reacts with  and forms deuterated acetylene.
and forms deuterated acetylene.
3. 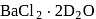 is an example of interstitial deuterate.
is an example of interstitial deuterate.
The correct statements are
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 16
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 17
Which of the following is an example of interstitial hydride?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 17
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 18
Which of the following is a salt-like hydride?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 18
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 19
Why is  preferred over
preferred over  as a moderator in nuclear reactors?
as a moderator in nuclear reactors?
 preferred over
preferred over  as a moderator in nuclear reactors?
as a moderator in nuclear reactors?
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 19
Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 20
Temporary hardness of water is removed in Clark's process by adding
Detailed Solution for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties - Question 20
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Information about Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Hydrides, Water and its Properties, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Download as PDF


 -block do not form hydrides at all. The inability of metals of group 7,8 and 9 of periodic table to form hydrides is referred to as hydrides gap of
-block do not form hydrides at all. The inability of metals of group 7,8 and 9 of periodic table to form hydrides is referred to as hydrides gap of 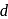 -block. In these compounds
-block. In these compounds  atoms are supposed to occupy interstitial position in the metal lattices. They are also called nonstoichiometric hydrides.
atoms are supposed to occupy interstitial position in the metal lattices. They are also called nonstoichiometric hydrides. and
and  which are covalent hydrides?
which are covalent hydrides? and
and  belong to
belong to  -block and since the electronegativity difference between these elements and
-block and since the electronegativity difference between these elements and  is very less, they form covalent hydrides.
is very less, they form covalent hydrides.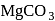 is insoluble in water.
is insoluble in water.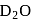 actually has higher freezing point
actually has higher freezing point  than water
than water 



 , high liquid range and can dissolve maximum number of compounds. That is why it is used as universal solvent.
, high liquid range and can dissolve maximum number of compounds. That is why it is used as universal solvent. is used for the softening of temporary hard water.
is used for the softening of temporary hard water.


 th in water.
th in water.
 is an example of inerstitial hydride while
is an example of inerstitial hydride while  and
and  are the examples of covalent hydride.
are the examples of covalent hydride.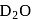 slows down the speed of neutrons more effectively than
slows down the speed of neutrons more effectively than  .
.















