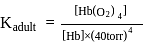Test: Le Chatelier's Principle - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Le Chatelier's Principle
In which of the following reactions, the equilibrium remains unaffected on addition of small amount of argon at constant volume?
For the formation of  from its constituent elements, the favourable conditions for its formation are
from its constituent elements, the favourable conditions for its formation are
 from its constituent elements, the favourable conditions for its formation are
from its constituent elements, the favourable conditions for its formation are| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For a reaction A(s) ⇌ B(s) + C(g) the set of all correct statements are
a) K is independent of [A].
b) K is dependent on partial pressure of C at a given temperature.
c) ΔH will be independent of temperature.
d) ΔH is independent of the catalyst addition.
a) K is independent of [A].
b) K is dependent on partial pressure of C at a given temperature.
c) ΔH will be independent of temperature.
d) ΔH is independent of the catalyst addition.
The % yield of ammonia as a function of time in the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g), ΔH < 0 at (P, T1) is given below

If this reaction is conducted at (P, T2), with T2 > T1, the %yield of ammonia as a function of time is represented by
Some inert gas is added at constant volume to the following reaction at equilibrium NH4HS(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + H2S(g)
Predict the effect of adding the inert gas:
The standard state Gibb's free energy change for the isomerisation reaction cis-2-pentene ⇌ trans-2-pentene is −3.67 kJ mol−1 at 400 K. If more trans-2-pentene is added to the reaction vessel
The equilibrium concentrations of  and
and  in the formation of
in the formation of  at
at  are
are  and
and 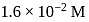 respectively. The equilibrium constant
respectively. The equilibrium constant  at the same temperature is
at the same temperature is
The reaction, SO2 + Cl2 ⟶ SO2Cl2 is exothermic and reversible. A mixture of 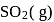 ,
, 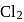 (g) and
(g) and  is at equilibrium in a closed container. Now a certain quantity of extra
is at equilibrium in a closed container. Now a certain quantity of extra  is introduced into the container, the volume remaining the same. Which of the following is are true?
is introduced into the container, the volume remaining the same. Which of the following is are true?
Why only  gets precipitated as
gets precipitated as  and not
and not  as
as  when
when 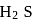 is passed through an acidic solution containing
is passed through an acidic solution containing  and
and  ?
?
Hemoglobin  protein transport
protein transport  in blood and each
in blood and each  can bind
can bind  , molecules. In discussing protein oxygen binding capacity, biochemists use a measure called the
, molecules. In discussing protein oxygen binding capacity, biochemists use a measure called the  value, defined as the partial pressure of oxygen at which
value, defined as the partial pressure of oxygen at which  of hemoglobin is saturated. Fetal hemoglobin has a
of hemoglobin is saturated. Fetal hemoglobin has a  value of
value of  torr and adult has
torr and adult has  value of
value of  torr. For the following equilibrium:
torr. For the following equilibrium:

What is the value of 
[Where K represents equilibrium constant.]
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|


 is a noble gas, it is also unreactive but it decreases the activation energy in both forward as well as backward directions by the same amount of reversible reaction.
is a noble gas, it is also unreactive but it decreases the activation energy in both forward as well as backward directions by the same amount of reversible reaction.
 No. of moles for forward reaction
No. of moles for forward reaction  for reactant and 2 for product
for reactant and 2 for product No. of moles for backward reaction
No. of moles for backward reaction  for reactant and 2 for product
for reactant and 2 for product
 No. of moles for forward reaction
No. of moles for forward reaction  for reactant and 1 for product
for reactant and 1 for product No. of moles for backward reaction
No. of moles for backward reaction  for reactant and 2 for product
for reactant and 2 for product
 No. of moles for forward reaction
No. of moles for forward reaction  for reactant and 2 for product
for reactant and 2 for product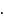 No. of moles for backward reaction
No. of moles for backward reaction  for reactant and 4 for product
for reactant and 4 for product takes place according to Le-Chatelier's principle.
takes place according to Le-Chatelier's principle.


 is a gas, so decrease in temperature will favour forward direction.
is a gas, so decrease in temperature will favour forward direction. .
.
 concentration of solid is considered as one during heterogenous equilibrium. So, as we can see
concentration of solid is considered as one during heterogenous equilibrium. So, as we can see  is independent of
is independent of  .
. So,
So,  is dependent on partial pressure of
is dependent on partial pressure of  .
. yield will also increase with time. But at equilibrium
yield will also increase with time. But at equilibrium  yield at high temperature
yield at high temperature  would be less than at
would be less than at  as reaction is exothermic so the graph is
as reaction is exothermic so the graph is
 equilibrium will shift to RHS which is exothermic. Hence temperature will increase.
equilibrium will shift to RHS which is exothermic. Hence temperature will increase. of
of 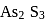 is less than
is less than 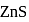 . In acidic medium ionisation of
. In acidic medium ionisation of 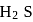 is suppresed (common ion effect) and
is suppresed (common ion effect) and  of
of  does not exceed.
does not exceed.