JEE Exam > JEE Tests > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - JEE MCQ
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - JEE MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides for JEE 2024 is part of Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced preparation. The Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides questions and answers have been
prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides below.
Solutions of Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides questions in English are available as part of our Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE & Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 1
Which of the following pairs of compounds are enantiomers?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 1
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 2
The correct order of SN2 E2 ration for the % yield of product of the following halide is

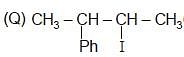
(R) CH3 — CH2 — I


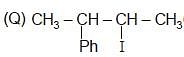

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 3
Among the following organic halides in the increasing order of their dehydrohalogenation reactions in the presence of alcoholic 
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 

(A)

(B)

(C)

(D)

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 3
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 4
Which one of the following is more reactive towards  reaction?
reaction?
 reaction?
reaction?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 4
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 5
Benzene reacts with  -propyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous
-propyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous  to give
to give
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 5
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 6
What is the product of the following reaction ?


Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 6
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 7
Identify  and
and  in the following reaction
in the following reaction

 and
and  in the following reaction
in the following reaction
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 7
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 8
Consider the reactions
(i)
(ii)
The mechanism of reactions (i) & (ii) are respectively
(i)

(ii)

The mechanism of reactions (i) & (ii) are respectively
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 8
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 9
How many stable alkenes on reaction with HCl will produce


Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 9
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 10
Number of ambidentate nucleophiles among the following 

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 10
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 11
Number of substrates which will show rearrangement is


Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 11
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 12

How many structures for  are possible?
are possible?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 12
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 13
Which one of the following compounds most readily undrgoes substitution by  mechanism?
mechanism?
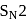 mechanism?
mechanism?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 13
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 14
Which of the following is fast debrominated?


Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 14
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 15
The organic compound (P) of the reaction:
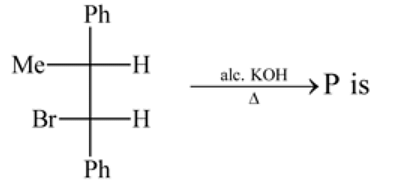
is
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 16
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 17
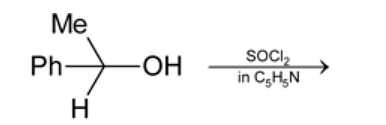
Which statement is true for the above reaction?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 17
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 18
On on heating diethyl ether with conc- HI, 2 moles of which of the following is formed
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 18
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 19
Alkyl halide reacts with an alcoholic solution of ammonia to give a mixture of:
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 19
Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 20
Product-I  Product-II The correct statement is
Product-II The correct statement is
 Product-II The correct statement is
Product-II The correct statement is
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides - Question 20
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Information about Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Preparation and Properties of Monohalides, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
Download as PDF




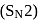 reaction involves reaction between reactant and nucleophile simultaneously without the formation of carbocation. Less hindered species are more reactive towards
reaction involves reaction between reactant and nucleophile simultaneously without the formation of carbocation. Less hindered species are more reactive towards 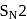 reaction. As
reaction. As  is least hindered alkyl halide, it will show more fast reaction towards
is least hindered alkyl halide, it will show more fast reaction towards  reaction.
reaction.

 .
.
 and
and 
 mechanism.
mechanism.


 mechanism is tert
mechanism is tert  alkyl halide
alkyl halide 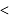 sec alkyl halide
sec alkyl halide 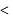 primary alkyl halide.
primary alkyl halide. mechanism.
mechanism.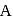 is also primary alkyl halide but in it, the carbon attached to is more hindered.
is also primary alkyl halide but in it, the carbon attached to is more hindered. undergoes elimination reactions. For example:
undergoes elimination reactions. For example:
 solution that functions as solvent gives alkoxide ions that act as a strong base. This base abstracts
solution that functions as solvent gives alkoxide ions that act as a strong base. This base abstracts  -Hydrogen atom from saturated substrate - alkyl halide.
-Hydrogen atom from saturated substrate - alkyl halide.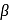 -Hydrogen atom is then transferred to the alkyl part to form an alkane and simultaneously a molecule of
-Hydrogen atom is then transferred to the alkyl part to form an alkane and simultaneously a molecule of  is eliminated.
is eliminated.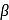 -hydrogen atoms of alkyl chloride to eliminate
-hydrogen atoms of alkyl chloride to eliminate  and form alkene.
and form alkene.








 (Product-I)
(Product-I) (Product-II)
(Product-II) (Product-I) isomer is
(Product-I) isomer is 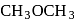
 denydration
denydration 















