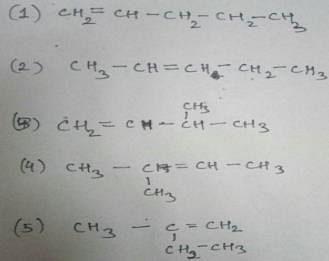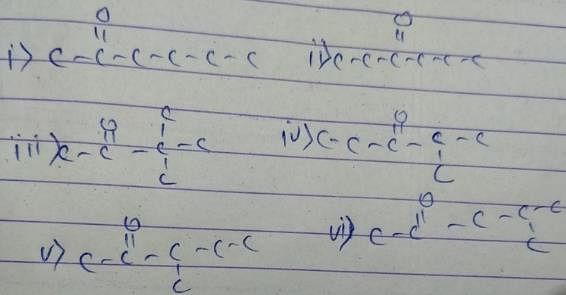Test: Structural Isomerism - NEET MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Structural Isomerism
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-18) This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
How many diffrent alkenes exist for C5H10 which are structural isomeres ?
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
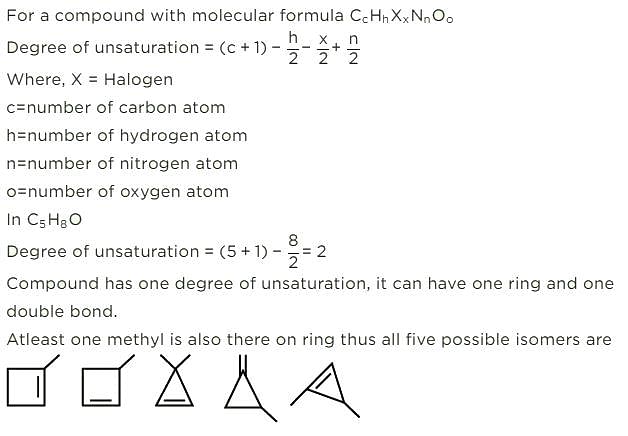
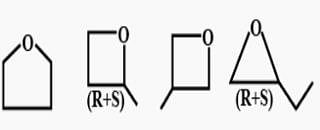
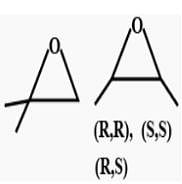
How many cycloalkene isomers exist for C5H8 which contain at least one methyl locant directly present on the ring?
Which of the following compounds will exhibit cis-trans isomerism?
How many structural isomers exist for C4 H80 which are simultaneously ether? Also there is no atom sp2-hybridised.
Organic compound with molecular formula C4H8O2 cannot have the functional group
How many structural isomers are possible with molecular formula C4H10O ?
How many structural isomers are possible for compounds containing C, H and O atoms only with their molar masses 100 as well as the isomers are simultaneously ketones ?
For which of the following parameters the structural isomers C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 would be expected to have the same values?
[AIEEE 2004]
Compounds which have same molecular formula but different structural formula is called
A monocarboxylic acid is a functional isomer os
[JEE Main 2013 Online Exam]
In allene (C3H4 ), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
[JEE Main 2014 Online Exam]
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. A pair of positional isomers differs in the position of the same functional group.
II. A pair of. structural isomers have the same relative molar mass.
Ill. A pair of functional group isomers belongs to different homologous series.
Which of the following statements regarding ethanoic acid and methyl methanoate are correct?
I. They are functional group isomers with molecular fo nula C2H4O2.
II. They belong to different homologous series.
Ill. They have different chemical properties.
Which of the following statements concerning 3,4-dibromo-1-pentene and 3,5-dibromo-2-pentene are correct?
(I) They have same molecular formula C5H8Br2
(II) They are positional isomers.
(III) They have similar chemical properties.
Which of the following compounds are structural isomers of C5H10O?
I. 2-methyl butanal
II. Propyl ethanoate
Ill. Pentanal
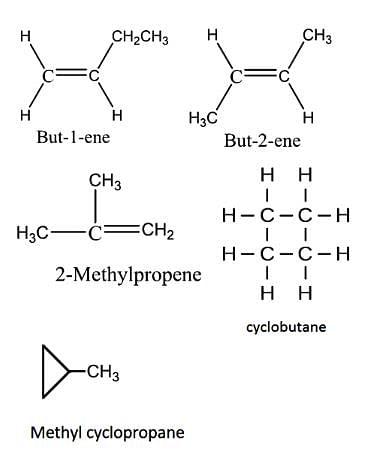
Constitutional isomerism is possible in alkenes only if the number of carbon atoms present is
|
129 videos|244 docs|88 tests
|