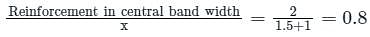Test: Footing & Rafts - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Foundation Engineering - Test: Footing & Rafts - 1
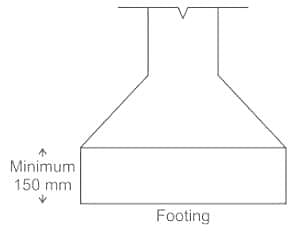
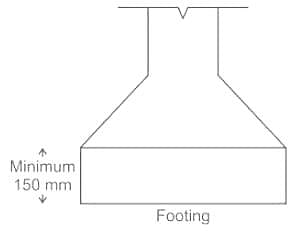
In a RCC footing on soil, the minimum thickness at edge should not be less than
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
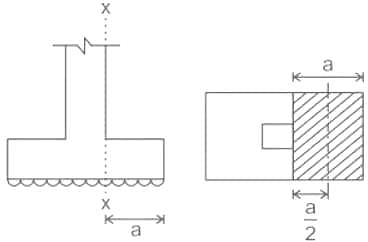
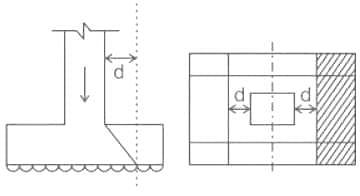
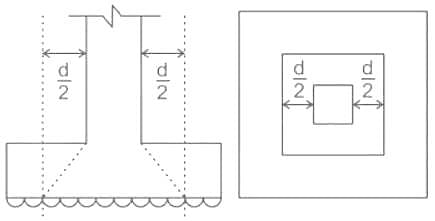
In case of a isolated square concrete footing, match the location at which the stress resultant are to be checked?


According to I.S. 456-1978, the thickness of reinforced concrete footing on piles at its edges is kept less than
In reinforced concrete footings, the minimum value of nominal cover for the reinforcing bar, to meet the durability requirement is:
The weight of the footing is assumed as ____ of the weight transferred to the column.
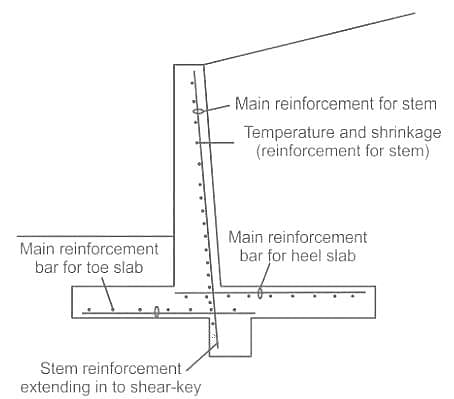
In R.C.C. cantilever retaining wall, if the check for overturning is not satisfied, which of the following would serve the better in meeting the check?
The height of a retaining wall is 5.5 m. It is to be designed as
In reinforced and plain concrete footing resting on soils, the thickness at edge shall not be less than:
For a RC footing ratio of its long side to short side is 1.5. The ratio of reinforcement to be provided in the central band width to total reinforcement in the short direction shall be:
|
18 videos|46 docs|27 tests
|
|
18 videos|46 docs|27 tests
|