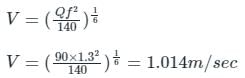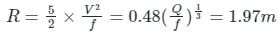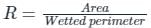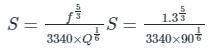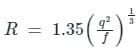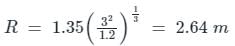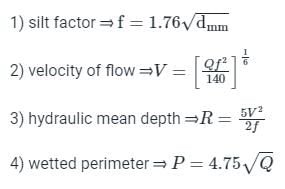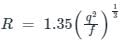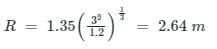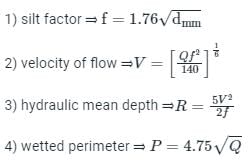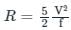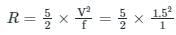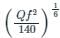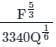Test: Design of Canals - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Irrigation Engineering - Test: Design of Canals
Which type of canal is not provided with any headwork for diversion of river water?
Design a regime channel for a discharge of 90 cumecs and silt factor is 1.3 use Lacey's Theory
In a navigation canal the velocity of the flowing water should be ____
Lacey's scour depth for a stream carrying a discharge of 3 cumecs/m width having a silt factor 1.2 is
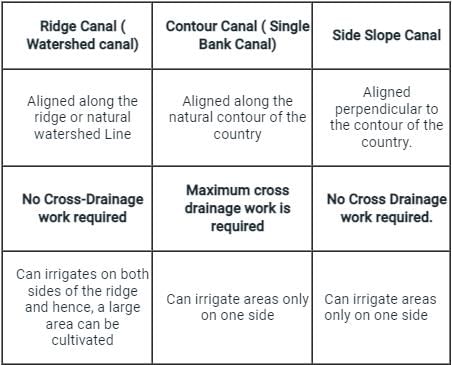
Among the classification of canals based on alignment criteria, identify the canal in which the number of cross drainage works is maximum?
Lacey’s scour depth for a stream carrying a discharge of 3 cumecs per meter width having a silt factor 1.2 is
Canal normally used for diversion of flood water of a river is ______.
An irrigation channel designed by Lacey’s theory has a mean velocity of 1.5 m/s. The silt factor is unity. The hydraulic mean radius will be:
|
7 videos|49 docs|31 tests
|