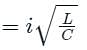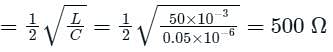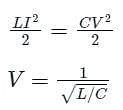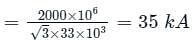Test: Circuit Breakers - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Power Systems - Test: Circuit Breakers
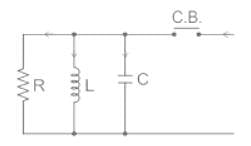
In a 132 kV system, the series inductance up to the point of circuit breaker location is 50 mH. The shunt capacitance at the circuit breaker terminal is 0.05 μF. The critical value of resistance required to be connected across the circuit breaker contacts which will given no transient oscillation is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
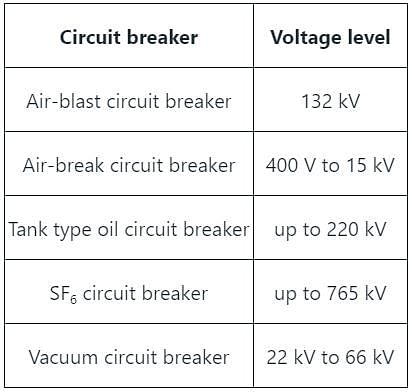
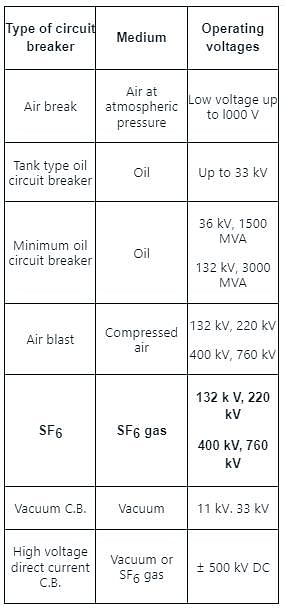
A vacuum circuit breaker can be used in which voltage range?
Which is the most serious problem in vacuum circuit breaker?
The highest rating of Triple pole with Neutral (TPN) MCB main switches available in the local market is _______.
For below 400 KV systems, the circuit breaker is designed to withstand ______above the normal system voltage.
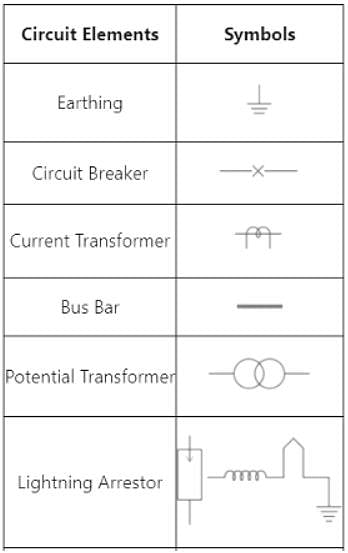
In relation to electrical drawing, the following symbol is used for?

The SF6 circuit breakers are preferred for the substation with:
The voltage that appears across the breaker contact after the circuit breaker is opened is called.
A three-phase 33 kV, oil-circuit breaker is rated 1500 A, 2000 MVA, 2 s. The symmetrical breaking current for this breaker would be
Which of the following could be the effect of using high-speed circuit breakers in a power system?
Arcing contacts of a circuit breaker is made by using __________.
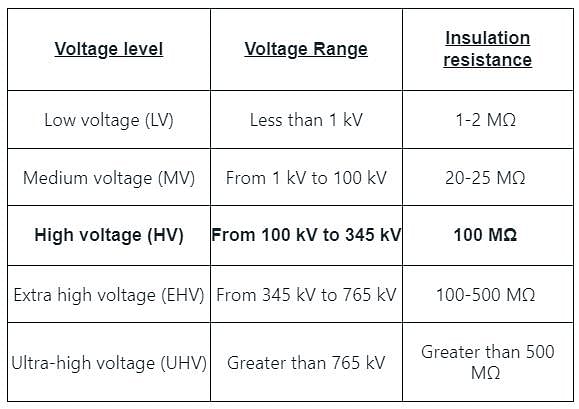
Insulation resistance of high voltage circuit breakers is more than
Which of the following voltage ranges is correct for using a vacuum circuit breaker?
|
21 videos|67 docs|45 tests
|
|
21 videos|67 docs|45 tests
|