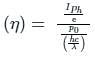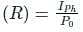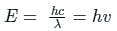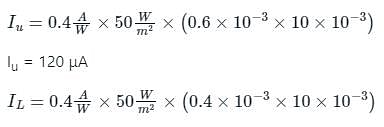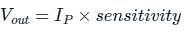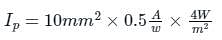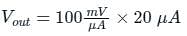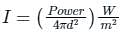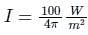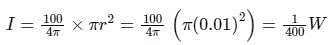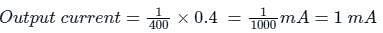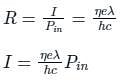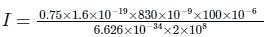Test: Photo Diode - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Electronic Devices - Test: Photo Diode
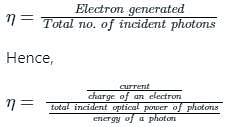
The quantum efficiency η for the photodetector is -
Where Iph = average photo current
Po = Average incident optical power
hc/λ = incident photon energy
Where Iph = average photo current
Po = Average incident optical power
hc/λ = incident photon energy
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which one of the following can be used as a photo detector in Fiber Optic Communication?
___ current is the leakage current that flows through a photo diode with no input used in as light detectors.
A light detector circuit using an ideal photo-diode is shown in the figure. The sensitivity of the photo-diode is 0.5 μA/μW. With Vr = 6 V, the output voltage Vo = −1.0 V for 10 μW of incident light. If Vr is changed to 3 V, keeping all other parameters the same, the value of Vo in volts is __________V.
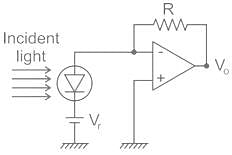
In the given circuit as the intensity of light falling on photodiode increases, the output voltage.
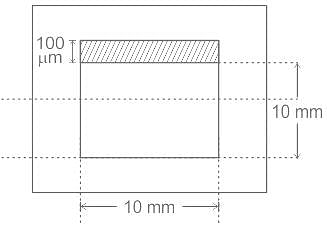
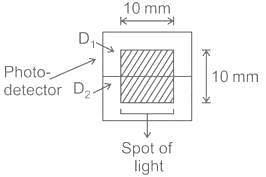
The figure shows a spot of light of uniform intensity 50 W/m2 and size 10 mm × 10 mm incident at the exact center of a photo-detector, comprising two identical photo-diodes D1 and D2. Each diode has a sensitivity of 0.4 A/W and is operated in the photoconductive mode. If the spot of light is displaced upwards by 100 μm, the resulting difference between the photocurrents generated by D1 and D2 in micro amperes, is __________ μA.
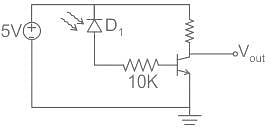
The photo diode in the figure below has an active sensing area of 10 mm2, a sensitivity of 0.5 A/W and a dark current of 1 µA. The i-to-v converter has a sensitivity of 100 mV/µA. For an input light intensity of 4 W/m2, the output VO in volt is ____.

A 100 W light source emits uniformly in all directions. A photodetector having a circular active area whose diameter is 2 cm is placed 1 m away from the source, normal to the incident light. If the responsivity of the photodetector is 0.4 A/W, the photo-current generated in the detector, in units of mA, is
Quantum efficiency of a photodiode (ratio between the number of liberated electrons and the number of incident photons) is 0.75 at 830 nm. Given Planck’s constant h = 6.624 × 10-34 J-sec, the charge of an electron e = 1.6 × 10-19 C and the velocity of light in the photodiode Cm = 2 × 108 m/s. For an incident optical power of 100 μW at 830 nm, the photocurrent in μA is __________.
|
21 docs|29 tests
|
|
21 docs|29 tests
|