BPSC Practice Test- 1 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test BPSC Prelims Mock Test Series & Past Year Papers 2024 - BPSC Practice Test- 1
Which of the following is one of the key objectives of Bihar Business Connect 2024?
Consider the following statements regarding PM Vishwakarma scheme.
- PM Vishwakarma scheme aims to help traditional craftspeople and artisans by providing interest-free loans.
- The scheme also aims at improving the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople.
- The scheme covers rural and urban areas across India.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following rivers is not a tributary of the Sone River?
Which of the following are the main sources of authentic history of the musical tradition of Mithila of Bihar?
Which one of the following is presided over by a person who is not its member?
Satapatha Brahmana and Taittiriya Brahmana are the Brahmin texts of which Veda?
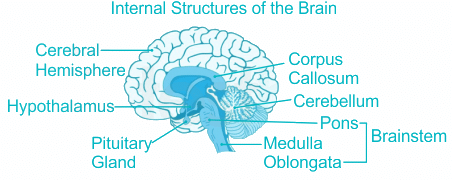
The respiratory centres which control inspiration and expiration are located in the
The main occupation of the people of the Indus Valley Civilization was ________.
Which one of the following is the chief characteristic of 'mixed farming'?
Who determines the centre - state financial relations from the following?
______ is the concentration of a toxin at successively higher levels in a food chain.
Who had invited Gandhiji in West Champaran district in Bihar?
Which among the following are the reasons for which Bihar adopted a child budget?
Study the following bar graph and answer the question that follows.
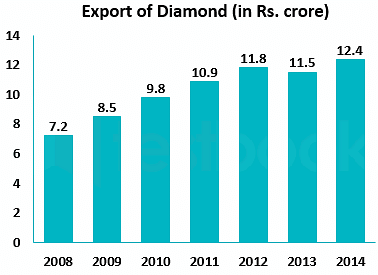
In how many years was the export more than the average for the given period?
Which of the following cities of Russia is known as the Venice of the North?
Under which of the following Acts, Dyarchy was introduced at Central level?
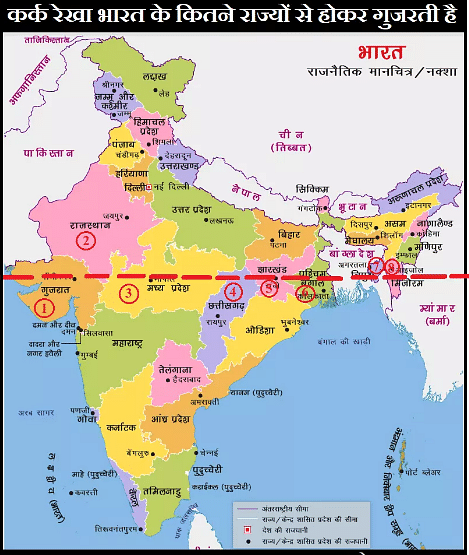
Tropic of Cancer passes through which of the following states?
1. Gujarat
2. Chhattisgarh
3.Uttar Pradesh
4. Jharkhand
Select the correct answer from the code given below:
Which of the following is NOT a pass in the Western Ghats Mountain ranges?
1. NABARD was established under the RBI Act of 1934.
2. NABARD provides financial support for urban infrastructure development.
3. NABARD operates as a statutory body.
4. NABARD was established in 1982.
|
3 docs|29 tests
|
|
3 docs|29 tests
|