Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Tests > Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 > Acids, Bases And Salts - Class 10 MCQ
Acids, Bases And Salts - Class 10 MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 - Acids, Bases And Salts
Acids, Bases And Salts for Class 10 2024 is part of Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 preparation. The Acids, Bases And Salts questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus.The Acids, Bases And Salts MCQs are made for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Acids, Bases And Salts below.
Solutions of Acids, Bases And Salts questions in English are available as part of our Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 for Class 10 & Acids, Bases And Salts solutions in
Hindi for Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Acids, Bases And Salts | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Class 10 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 for Class 10 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
*Multiple options can be correct
Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 1
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube?
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 1
Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 2
When hydrogen chloride gas is prepared on a humid day, the gas is usually passed through the guard tube containing calcium chloride. The role of calcium chloride taken in the guard tube is to
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 5
Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 6
At what temperature is gypsum heated to form Plaster of Paris?
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 7
Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 8
Which of the following statements is correct about an aqueous solution of an acid and of a base?
(i) Higher the pH, stronger the acid
(ii) Higher the pH, weaker the acid
(in) Lower the pH, stronger the base
(iv) Lower the pH, weaker the base
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 8
*Multiple options can be correct
Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 9
The apparatus given in the adjoining figure was set up to demonstrate electrical conductivity.
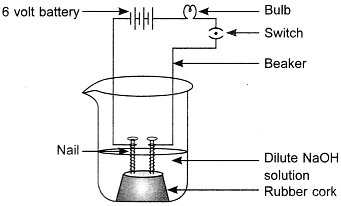
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
Detailed Solution for Acids, Bases And Salts - Question 10
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|
Information about Acids, Bases And Salts Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Acids, Bases And Salts solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Acids, Bases And Salts, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|
Download as PDF

















