Test: Engineering Mechanics - 5 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Additional Study Material for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Engineering Mechanics - 5
According to principle of conservation of energy, the total momentum of a system of masses in any direction remains constant unless acted upon by an external force in that direction.
The friction experienced by a body, when in motion, is known as
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two balls of equal mass and of perfectly elastic material are lying on the floor. One of the ball with velocity v is made to struck the second ball. Both the balls after impact will move with a velocity
The term 'force' may be defined as an agent which produces or tends to produce, destroys or tends to destroy motion.
The coefficient of restitution for elastic bodies is one.
The velocity ratio in case of an inclined plane inclined at angle θ to the horizontal and weight being pulled up the inclined plane by vertical effort is
The range of projectile on a downward inclined plane is __________ the range on upward inclined plane for the same velocity of projection and angle of projection.
The angle of inclination of a vehicle when moving along a circular path __________ upon its mass.
A body of weight W is required to move up on rough inclined plane whose angle of inclination with the horizontal is α. The effort applied parallel to the plane is given by(where μ = tanφ = Coefficient of friction between the plane and the body.)
If the resultant of two equal forces has the same magnitude as either of the forces, then the angle between the two forces is
A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains in __________ equilibrium.
Coefficient of friction is the ratio of the limiting friction to the normal reaction between the two bodies.
Moment of inertia of a circular section about an axis perpendicular to the section is
The time of flight (t) of a projectile on an upward inclined plane is(where u = Velocity of projection, α = Angle of projection, and β = Inclination of the plane with the horizontal.)
Moment of inertia of a triangular section of base (b) and height (h) about an axis passing through its C.G. and parallel to the base, is
If the masses of both the bodies, as shown in the below figure, are reduced to 50 percent, then tension in the string will be 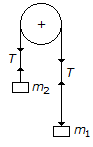
Which of the following is an equation of linear motion?(where, u and v = Initial and final velocity of the body, a = Acceleration of the body, and s = Displacement of the body in time t seconds.)
If a number of forces are acting at a point, theirresultant will be inclined at an angle θ with the horizontal, such that
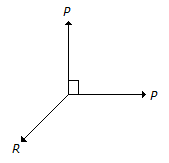
The above figure shows the two equal forces at right angles acting at a point. The value of force R acting along their bisector and in opposite direction is
The force required to move the body up the plane will be minimum if it makes an angle with the inclined plane __________ the angle of friction.
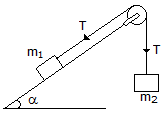
In the shown figure, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased, then acceleration of the system will
The total time taken by a projectile to reach maximum height and to return back to the ground, is known as time of flight.
The frequency of oscillation of a torsional pendulum is
The range of a projectile is maximum, when the angle of projection is
|
1 videos|30 docs|57 tests
|
|
1 videos|30 docs|57 tests
|

















