31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Molecular Basis of Inheritance - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Molecular Basis of Inheritance - 1
The lactose present in the growth medium of bacteria is transported to the cell by the action of (NEET 2024)
Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)
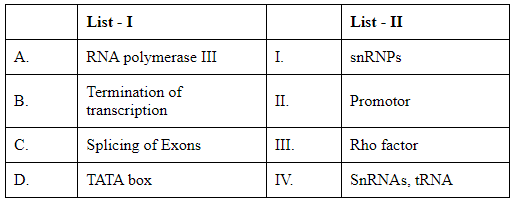
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which one is the correct product of DNA dependent RNA polymerase to the given template? (NEET 2024)
3'TACATGGCAAATATCCATTCA5'
Which of the following statement is correct regarding the process of replication in E.coli? (NEET 2024)
Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)
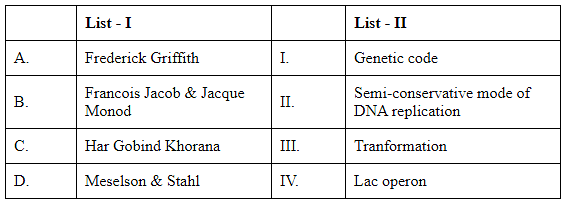
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by the three regions in DNA and these are with respect to upstream and down stream end; (NEET 2024)
Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)
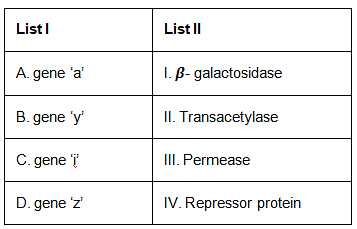
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: In prokaryotes, the positively charged DNA is held with some negatively charged proteins in a region called nucleoid.
Statement II: In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Upon exposure to UV radiation, DNA stained with ethidium bromide will show (NEET 2023)
Unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material was first proposed by (NEET 2023)
What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in Eukaryotes? (NEET 2023)
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to (NEET 2023)
If a geneticist uses the blind approach for sequencing the whole genome of an organism, followed by assignment of function to different segments, the methodology adopted by him is called as : (NEET 2022)
Transposons can be used during which one of the following? (NEET 2022)
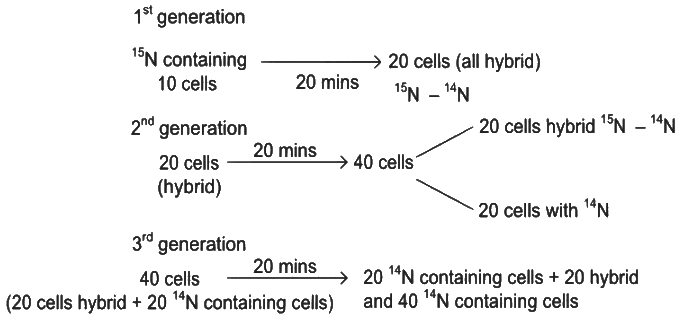
Ten E.coli cells with 15N - dsDNA are incubated in medium containing 14N nucleotide. After 60 minutes, how many E.coli cells will have DNA totally free from 15N? (NEET 2022)
If the length of a DNA molecule is 1.1 metres, what will be the approximate number of base pairs? (NEET 2022)
In lac operon, z gene codes for (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
The process of translation of mRNA to proteins begins as soon as: (NEET 2022)
Against the codon 5' UAC 3', what would be the sequence of anticodon on tRNA? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
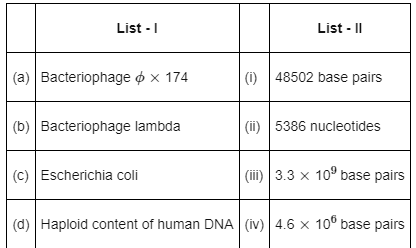
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
DNA Polymorphism forms the basis of: (NEET 2022)
Given below are two statements (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Statement I : DNA polymerases catalyse polymerisation only in one direction, that is 5' → 3'.
Statement II : During replication of DNA, on one strand the replication is continuous while on other strand it is discontinuous.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Read the following statements and choose the set of correct statements: (NEET 2022)
(A) Euchromatin is loosely packed chromatin
(B) Heterochromatin is transcriptionally active
(C) Histone octomer is wrapped by negatively charged DNA in nucleosome
(D) Histones are rich in lysine and arginine
(E) A typical nucleosome contains 400 bp of DNA helix
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In an E. coli strain, i gene gets mutated, and its product cannot bind the inducer molecule. If the growth medium is provided with lactose, what will be the outcome? (NEET 2022)
Match List - I with List - II. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
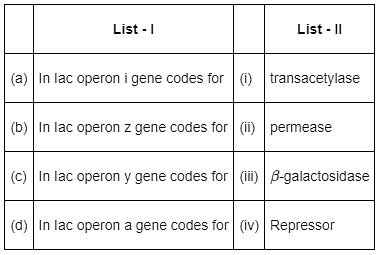
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes? [2021]
Name the enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription. [2020]
Which of the following features of genetic code does allow bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology? [2019]
The experimental proof for semi-conservative replication of DNA was first shown in a [2018]
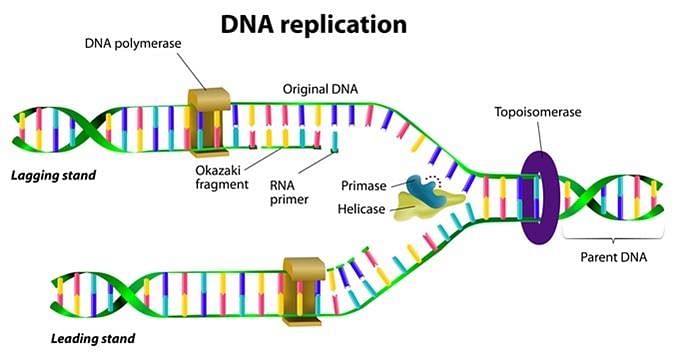
During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are used to elongate [2017]
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|