31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Respiration in Plants - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Respiration in Plants - 1
Which of the following statements is incorrect? [2021]
The number of substrate level phosphorylations in one turn of citric acid cycle is : [2020]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, the first irreversible reaction of glycolysis, is catalysed by [2019]
The three boxes in this diagram represents the three major biosynthetic pathways in aerobic respiration. Arrows represents net reactants or products. [NEET 2013]
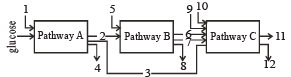
Arrows numbered 4, 8 and 12 can all be :
Which of the metabolites is common to respiration mediated breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins? [NEET 2013]
The energy - releasing metabolic process in which substrate is oxidised without an external electron acceptor is called: [2010]
Aerobic respiratory pathway is appropriately termed: [2009]
The chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis of oxidative phosphorylation proposes that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is formed because: [2008]
In germinating seeds fatty acids are degraded exclusively in the [2008]
The energy-releasing process in which the substrate is oxidised without an external electron acceptor is called [2008]
The overall goal of glycolysis, krebs cycle and the electron transport system is the formation of[2007]
All enzymes of TCA cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix except one which is located in inner mitochondrial membranes in eukaryotes and in cytosol in prokaryotes. This enzyme is [2007]
The bacterium (Clostridium botulinum) that causes botulism is [2006]
How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one mole of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one mole of ATP is 12 kcal ? [2006]
During the stage in the complete oxidation of glucose are the greatest number of ATP molecules formed from ADP [2005]
Chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in the chloroplasts and mitochondria is based on:[2005]
In glycolysis, during oxidation electrons are removed by [2004]
n which one of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing ? [2003]
Which one of the following concerns photophosphorylation ? [2003]
During anaerobic digestion of organic waste, such as in producing biogas, which one of the following is left undegraded ? [2003]
In alcoholic fermentation [2003]
How many ATP molecules are produced by aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose? [2002]
Net gain of ATP molecules during aerobic respiration is [1999]
Maximum usable energy per mol of glucose metabolised will be generated during [1999]
Site of respiration in bacteria is [1997]
In Krebs cycle FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of [1997]
The mechanism of ATP formation both in chloroplast and mitochondria is explained by[1997]
Fermentation is anaerobic production of [1996]
Krebs cycle occurs in [1996]
The enzymes hexokinase which catalyses glucose to glucose-6-phosphate in glycolysis is inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate. This is an example of [1996]
|
33 docs|83 tests
|
|
33 docs|83 tests
|

















