Test: Anatomy of Dicotyledonous & Monocotyledonous Plants (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Anatomy of Dicotyledonous & Monocotyledonous Plants (NCERT)
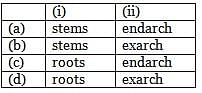
In (i) protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies towards centre. Such an arrangement of primary xylem is called as (ii)

Casparian strips are the bands of thickenings present on _____ walls of endodermis.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which plant part possesses polyarch condition of vascular bundles with a well developed pith?
Hypodermis is _______ in sunflower stem and _______in maize stem.
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
Refer the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.


Well develped pith is found in
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the______ surfaces.
Which of the following conditions of xylem is present in both monocot and dicot stems?
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of Isobllateral leal.
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are ________ and ________ respectively.
What type of parenchyma is situated below the palisade cells in leaf anatomy?
What type of tissue surrounds each vascular bundle in a monocot stem?
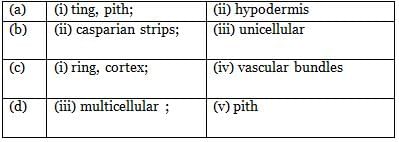
Read the following statements with 1-2 blanks in each one of them.
(i) In monocot root, a large number of vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a _____ around the cent
(ii) Due to the presence of the endodermal cells do not allow wall to wall movement of substances between cortex and peticyde, in a primary dicot toot.
(iii) The epidermis of stem of sunflower beats several unbranched ________ hair.
(iv) The central portion of a dicot stem is usually occupied by ________ comprising of thin walled parenchymatous cells.
Fill in the blanks in the above statements and select the correct option for any two of them.
Vascular bundle is enclosed with in a well developed sderenchymatous sheath in
A typical monocotyledonous root is characterized by
Read the following statements.
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eustele
Above given features describe which of the following plant parts?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
Where is the phloem usually located in conjoint vascular bundles found in stems and leaves?
|
182 videos|367 docs|152 tests
|

















