R.C. Mukherjee Test: Solutions - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - R.C. Mukherjee Test: Solutions
Total vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mol volatile component A(pºA = 100 mmHg) and 3 mol of volatile component B (pºB = 60 mmHg) is 75 mm. For such case -
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by
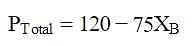
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
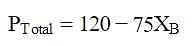
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
Van't Hoff factors of aqueous solutions of X, Y, Z are 1.8, 0.8 and 2.5. Hence, their (assume equal concentrations in all three cases) then correct order is :-
Decimolar solution of potassium ferricyanide, K3[Fe(CN)6] has osmotic pressure of 3.94 atm at 27ºC. Hence percent ionisation of the solute is -
An aqueous solution of urea containing 18 g urea in 1500 cm3 of solution has a density of 1.052 g/cm3. If the molecular weight of urea is 60, then the molality of solution is-
2.56 g of sulphur in 100 g of CS2 has depression in f.p. of 0.010º, Kf = 0.1º (molal)-1. Hence, atomicity of sulphur is -
Consider following solutions -
I : 1 M a glucose II. : 1 M a sodium chloride
III. : 1 M benzoic acid in benzene IV. : 1 M ammonium phosphate
Select incorrect statement -
The relationship between osmotic pressure at 273 K when 10 g glucose (P1) 10 g urea (P2) and 10 g sucrose (P3) are dissolved in 250 ml of water is -
The osmotic pressure of a solution of benzoic acid dissolved in benzene is less than expected because-
Assuming each salt to be 90% dissociated, which of the following will have highest osmotic pressure
Which one of the following pairs of solution can we expect to be isotonic at the same temperature-
For a solution containing non-volatile solute, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is 0.2. If the solution contains 5 moles in all, which of the following are true ?
I. Mole fraction of solute in the solution is 0.2
II. No. of moles of solute in the solution is 0.2
III. No. of moles of solvent in the solution is 4
IV. Mole fraction of solvent is 0.2 -
A complex containing K+, Pt (IV) and Cl- is 100% ionised giving i = 3. Thus, complex is
If pKa = -log Ka = 4, and Ka = Cα2 then van't Hoff factor for weak monobasic acid when C = 0.01 M is-
pH of 1M HA (weak acid) is 2. Hence van't Hoff factor is -
If 18 gram of glucose (C6H12O6) is present in 1000 gram of an aqueous solution of glucose it is said to be-
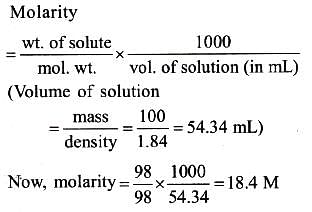
What is the molarity of H2SO4 solution that has a density of 1.84 gm/cc at 350C and contains 98% by weight-
In order to prepare 100 cm3 of 0.250 M barium chloride solution the amount of BaCl2.2H2O required will be-
25 mL of 3 M HCl were added to 75 mL of 0.05 M HCl. The molarity of HCl in the resulting solution is approximately-
0.2 mole of HCl and 0.1 mole of CaCl2 were dissolved in water to have 500 ml of solution, the molarity of Cl¯ ions is-
When 5.0 gram of BaCl2 is dissolved in water to have 106 gram of solution. The concentration of solution is-
For an ideal binary liquid solution with , which relation between XA(molefraction of A in liquid phase) and YA (mole fraction of A in vapour phase) is correct?
Mole fraction of A vapours above the solution in mixture of A and B(XA = 0.4) will be
[Given : = 100 mm Hg and
= 200 mm Hg]
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is
A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid A ( = 100 mm Hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid B(= 80 mmHg). If solution behaves ideally, the total vapour pressure of the distillate is
Which of the following aqueous solution will show maximum vapour pressure at 300 K?
The Van't Hoff factor for a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is
The correct relationship between the boiling points of very dilute solution of AlCl3(T1K) and CaCl2(T2K) having the same molar concentration is
|
100 videos|282 docs|123 tests
|