Test: Blood (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Blood (NCERT)
Which one of the following statements is correct with regardto the principle of safe blood transfusion?
A drop of each of the following is placed separately onfour slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
In which of the following situations, there is a risk factorfor children acquiring erythroblastosis foetalis?
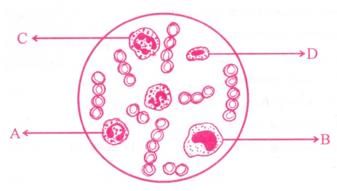
Study the given figure and identify the cells labelled as A, B, C and D.
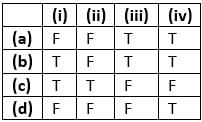
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F)?
I. Proteins contribute 6-8% of the blood plasma
II. Plasma contains very high amount of minerals
III. Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum
IV. Glucose, amino acids, lipids, etc., are also present in the plasma as they are always in transit in the body.
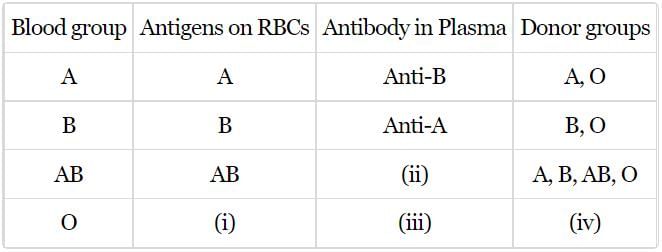
In the following table of human ABO blood groups fill-up the blanks (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) front the options}; below.
Find the correct descending order of percentage proportion of leucocytes in human blood.
Consider the following statements (A-C) each with one or two blanks.
(A) (1) are the most abundant cells (60-65 percent) of the total WBCs and (2) are the least (0.5-1 percent) among them.
(B) Platelets are cell fragments produced from (3).
(C) During clot formation, fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive (4) in the plasma by the enzyme (5)
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements ?
A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the doctor?
Which of the following blood groups is a universal recipient in blood transfusion?
Which of the following statements regarding erythrocytes and leucocytes is/are correct?
i. Erythrocytes are nucleated cells that transport respiratory gases.
ii. A healthy adult has approximately 5 million to 5.5 million erythrocytes per mm³ of blood.
iii. Neutrophils are the most abundant type of leucocytes, constituting 60-65% of total WBCs.
iv. Leucocytes contain haemoglobin, which gives them their color.
Which of the following statements about the functions and characteristics of blood cells is/are correct?
i. Basophils are the most abundant type of WBCs and play a major role in phagocytosis.
ii. Eosinophils help in resisting infections and constitute 2-3% of total WBCs.
iii. The average lifespan of erythrocytes is about 120 days before being destroyed in the liver.
iv. Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms entering the body.
|
180 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|



















