Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - 2 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - 2
Two animal cells are interconnected by
Which of the following leucocytes transforms into macrophages?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The type of connective tissue that is associated with the umbilical cord is
Read the following statements and answer the question.
(i) It is made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries.
(ii) They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs.
(iii) They are involved in forming a diffusion boundary.
Which of the following tissue is being described by the above statements?
The haemoglobin content/100 ml of blood of a normal healthy human adult is
A student was given a sample of two tissues. He observed the tissues under the microscope and draws their figures as 1 and 2 given below.

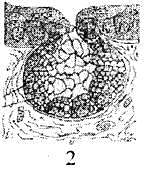
Identify the tissues 1 and 2.
Which one of the following is not a connective tissue?
The bone of a mammal contains Haversian canals which are connected by transverse canals known as:
The correct order of digestive system of frog is
The epithelium found in proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of nephron in the kidney is
The cell lining the blood vessels are
Blood plasma is pale yellow in colour due to
Choose the odd pair out in the following
Cartilage tissues are generally slow to heal injury because:
The special venous connection between liver and intestine as well as the kidney and lower parts of the body present in frogs is called
Which make up more than one-half the volume of neural tissue in our body?
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|

















