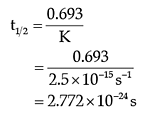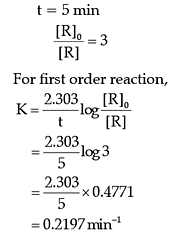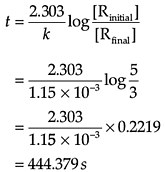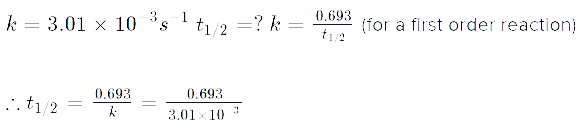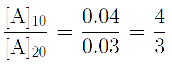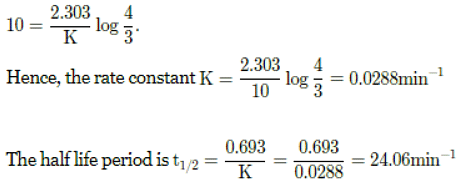Case Based Questions Test: Chemical Kinetics - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Case Based Questions Test: Chemical Kinetics
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Rate of reaction is a measure of change in concentration of reactant with respect to time.
Reason: Rate of reaction is a measure of change in concentration of product with respect to time.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: The unit of k is independent of order of reaction.
Reason: The unit of k is moles L–1s–1.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: For a reaction: P + 2Q → Products, Rate = k [P]1/2[Q]1 so the order of reaction is 1.5
Reason: Order of reaction is the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Reactions can occur at different speeds.
Reason: Rate of reaction is also called speed of reaction.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. Find the order of reaction:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The half-life for the reaction is:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The rate law equation is:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The rate constant of the reaction after 5 minutes is:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. How long will 5g of this reactant take to reduce to 3g?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. Under which condition a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. When the rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. For a reaction,
A + H2O → B
Rate ∝ [A]
The order of the reaction is:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half, i.e.,
[A]t = [A]/2
For first order reaction,
t1/2 = 0.693/k
This means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration. Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.
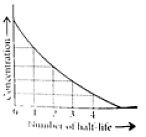
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. A first order reaction has a rate constant k = 3.01 x 10-3 /s. How long it will take to decompose half of the reactant?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half, i.e.,
[A]t = [A]/2
For first order reaction,
t1/2 = 0.693/k
This means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration. Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.
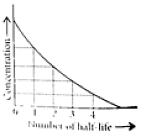
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. For the half-life period of a first order reaction, which one of the following statements is generally false?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half, i.e.,
[A]t = [A]/2
For first order reaction,
t1/2 = 0.693/k
This means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration. Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The rate of a first order reaction is 0.04 mol L-1 s-1 at 10 minutes and 0.03 mol L-1 s-1 at 20 minutes after initiation. The half life of the reaction is
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|