Case Based Questions Test: Amines - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Case Based Questions Test: Amines
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3 is the order of basic strength in case of methyl substituted amines.
Reason (R): The inductive effect, solvation effect and steric hindrance of the alkyl group decides the basic strength of alkyl amines in the aqueous state.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): Amines behave as a Lewis base.
Reason (R): Amines have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): (C2H5) 2NH > (C2H5) 3N > C2H5NH2 > NH3 is the order of basic strength in case of ethyl substituted amines.
Reason (R): The change of nature of the alkyl group, does not result in change of the order of basic strength.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger is the corresponding amine as a base.
Reason (R): The order of basicity of aliphatic amines is: primary > secondary > tertiary.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
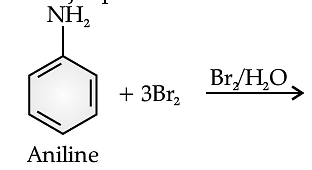
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): Benzene ring is aniline is highly deactivated.
Reason (R): In aniline, the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring increases the electron density on the ring.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): The amino group of aniline is acetylated before bromination.
Reason (R): It is due to the strong deactivating effect of –NH2 group.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): In aniline –NH2 group facilitates the electrophilic attack.
Reason (R): It is due to decrease in electron density on the ring.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): In aniline, the substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions.
Reason (R): The electron density is more at ortho and para positions.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. Give the major product of the following reaction:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
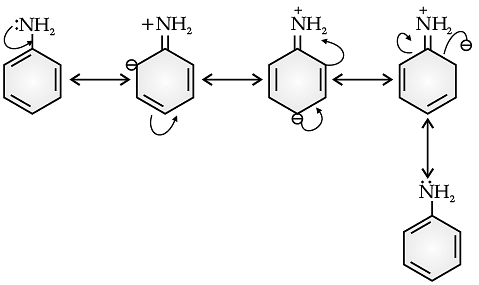
Q. Aniline is a resonance hybrid of
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. What is the major product A of the following reaction:

Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. Why is the activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group in the above reaction less than the activating effect of amino group?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A mixture of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) was separated by dissolving in chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound (A), when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produce C7H5N (C) associated with unpleasant odour.
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. Direct nitration of an aromatic compounds (A) is not feasible because
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A mixture of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) was separated by dissolving in chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound (A), when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produce C7H5N (C) associated with unpleasant odour.
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. What is A?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A mixture of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) was separated by dissolving in chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound (A), when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produce C7H5N (C) associated with unpleasant odour.
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The alkaline aqueous layer (B) when heated with chloroform and then acidified give a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2. (B) is
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|