Test: Biology Minor Mock Test- 3 (March 21) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Biology Minor Mock Test- 3 (March 21)
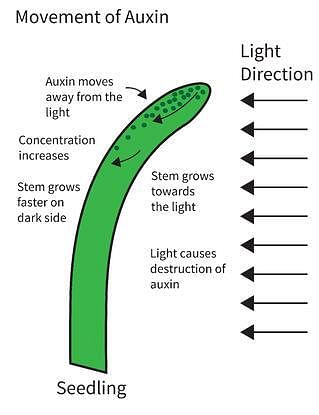
Example of artificial auxins are:
(a) IPA
(b) PAA
(c) NAA
(d) 2, 4, 5 - T
(e) 2, 4 - D
(b) PAA
(c) NAA
(d) 2, 4, 5 - T
(e) 2, 4 - D
What is the significance of cytokinins in plant development?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is essential for fruit ripening?
Which of the following effects of auxins is of wide application?
Expiratory muscles contract at the time of
Which of the following is not a characteristic of alveoli?
In the process of transport of CO2 which phenomenon occurs between RBCs and plasma
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is
For proper transport of O2 and CO2 blood should be
Oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve will shift to right on decrease of
Which one of the following statement is correct?
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates is/are :
Which of the following blood components play a major role in blood coagulation?
In the systemic circulation, the blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to the liver is named:
The pre-hypertension blood pressure value is a measurement between:
The statement incorrect about the human heart is:
The cardiovascular centre is located in:
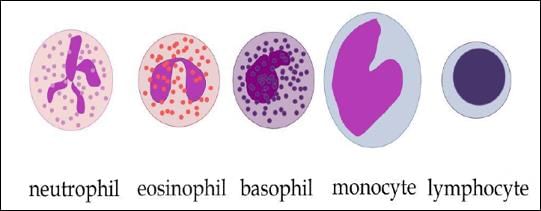
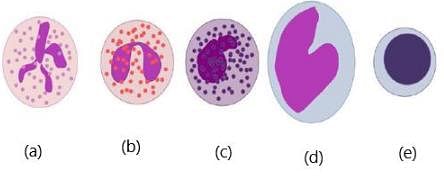
Where (a) is a neutrophil, identify the other four WBCs?
The layer of heart pericardium which checks its overstretching and overfilling as well as also protects the heart from mechanical injury is:
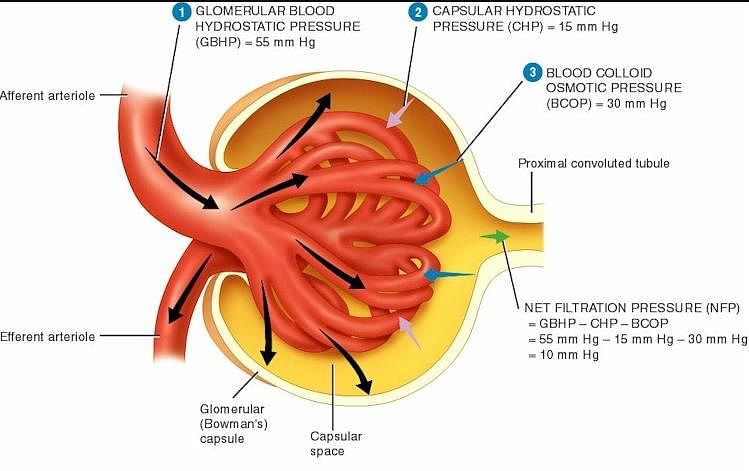
Blood enters glomerular capillaries through _____ arteriole and leaves through _____ arteriole:
The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form among them?
During micturition, the muscles of urinary bladder and urethral sphincters will
|
12 docs|366 tests
|