Test: Regulation of Gene expression & Human Genome Project (December 18) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Regulation of Gene expression & Human Genome Project (December 18)
During expression of an operon, RNA polymerase binds to
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given :
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
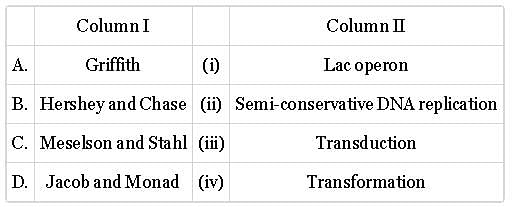
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
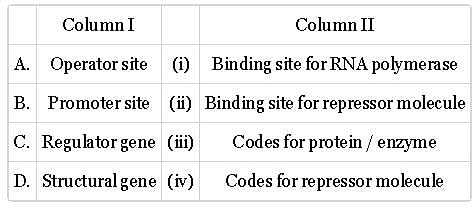

Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
The given figure shows lac operon and its functioning. Select the option which correctly labels A, B, X, Y and Z.
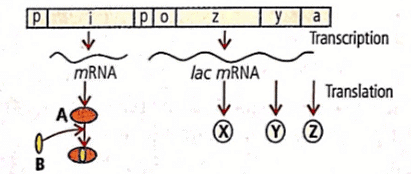
Regulation of gene expression occurs at the level of
Each species has a characteristic set of chromosome number called
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are methods for
Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced?
What is it that forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
In genetic fingerprinting, the ‘probe’ refers to
|
12 docs|366 tests
|

















