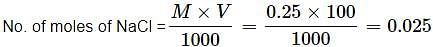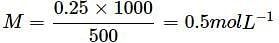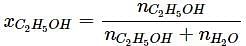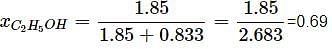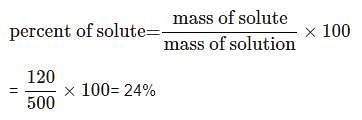Test: Chemistry Minor Mock Test- 2 (March 19) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Chemistry Minor Mock Test- 2 (March 19)
The specific conductances of four electrolytes in ohm−1cm−1 are given below. Which one offers higher resistance to passage of electric current?
The elements of group 14 are slightly more electronegative than group 13 elements because of
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How many Na+ ions are present in 100 mL of 0.25 M of NaCl solution?
For nth order reaction,
Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)
Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order
In the reaction of metallic cobalt placed in nickel sulphate solution, therein is a competition for release of electrons At equilibrium, chemical tests reveal that both Ni+2 (aq) and Co+2 (aq) are present at moderate concentrations. The result is that:
Chlorine, bromine and iodine when combined with oxygen, have oxidation numbers
In a free radical reaction, free radicals are formed at
The rate equation for the reaction,
2A + B → C
is found to be, rate = k[A] [B]
Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
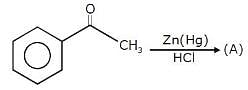
Which among the following is a very unstable and reactive species:
The function of Fe (OH)3 in the contact process is
Which of the following ions is most stable?
Among the following which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of B is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
The correct order of equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of LiCl, NaCl and KCl is:
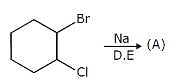
Mono-chloro product (inculding steroisomers)are :
What is the molarity of a solution containing 10 g of NaOH in 500 mL of solution?
Which of the following statements appears to the first order reaction?
2N2O5(CCl4) → 4NO2(CCl4) + O2(g)
What will be the mole fraction of ethanol in a sample of spirit containing 85% ethanol by mass?
Calculate the percentage composition of a solution obtained by mixing 200 g of a 20% and 300 g of a 30% solution by weight.
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen is an example of
Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
A compound X, of boron reacts with NH3 on heating to give another compound. Y which is called inorganic benzene. The compound X can be prepared by treating BF3 with Lithium aluminium hydride. The compounds X and Y are represented by the formulas.
In general, nonmetals as compared to metals have
The standard reduction potentials E°, for the half reactions are as:
The emf for the cell reaction,
Heterolytic cleavage is a way to cleave the:
|
12 docs|366 tests
|