Assertion & Reason Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - 2 - NEET MCQ
9 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - 2
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : SN2 reaction of an optically active aryl halide with an aqueous solution of KOH always gives an alcohol with opposite sign of rotation.
Reason : SN2 reactions always proceed with inversion of configuration.
Assertion : SN2 reaction of an optically active aryl halide with an aqueous solution of KOH always gives an alcohol with opposite sign of rotation.
Reason : SN2 reactions always proceed with inversion of configuration.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Exposure of ultraviolet rays to humans causes skin cancer, disorder and disrupts the immune system.
Reason : Carbon tetrachloride is released into air it rises to the atmosphere and depletes the ozone layer.
Assertion : Exposure of ultraviolet rays to humans causes skin cancer, disorder and disrupts the immune system.
Reason : Carbon tetrachloride is released into air it rises to the atmosphere and depletes the ozone layer.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : CCl4 is not a fire extinguisher.
Reason : CCl4 is insoluble in water.
Assertion : CCl4 is not a fire extinguisher.
Reason : CCl4 is insoluble in water.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Addition of bromine to trans-2-butene yields meso-2, 3-dibromobutane
Reason: Bromine addition to an alkene is an electrophilic addition.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: CCl4 is not a fire extinguisher.
Reason: CCl4 is insoluble in water.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Alkyl halides form alkenes when heated above300∘C.
Reason: CH3CH2I react slowly with strong base when compared to CD3CH2I.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: 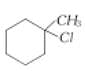 is less reactive
is less reactive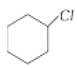 than towards reactions.
than towards reactions.
Reason: Tertiary alkyl halides react predominantly by SN1 mechanism.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Aryl halides undergo electrophilic substitutions more readily than benzene.
Reason: Aryl halide gives a mixture of o- and p- products.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Optically active 2-iodobutane on treatment with NaI in acetone undergoes racemization.
Reason: Repeated Walden inversions on the reactant and its product eventually gives a racemic mixture.
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|


 is more reactive than
is more reactive than 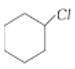 because the former is a tertiary alkyl halide and the latter is a secondary alkyl halide. Tertiary alkyl halides react predominantly by SN1 mechanism.
because the former is a tertiary alkyl halide and the latter is a secondary alkyl halide. Tertiary alkyl halides react predominantly by SN1 mechanism.














