Test: Geometrical Isomerism - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Geometrical Isomerism - 2
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
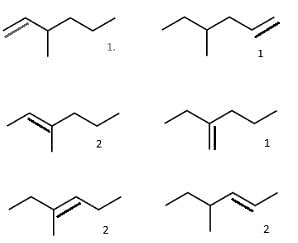
How many different stereoisomers exist for the compound shown?
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
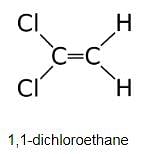
Which compound below is capable of showing geometrical isomerism ?
consider the following reaction.
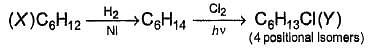
How many different isomers of X satisfy the above condition ?
Which isomer below has a stable intramolecular H-bond?
A ketone with molar mass of 100 g, has only one positional isomer. How many different enol isomers exist for this ketone?
Carbonyl compound condenses with ammonia as
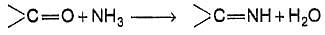
How many diffrent dilimines would be obtained on condensation of 2,4- pentanedlone with excess of ammonia ?
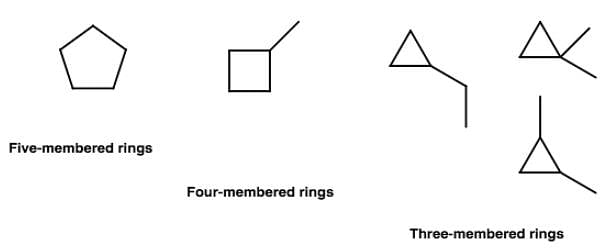
How many cyclic Isomers (structural and geometrical only) exist for C5H10?
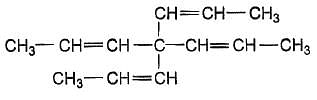
How many geometrical isomers exist for the molecule shown below ?
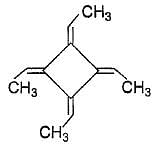
If chlorocyclohexane is subjected to further chlorination, how many different isomers (geometrical plus structural only) of dichiorocyclohexane would be produced?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-18) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q.
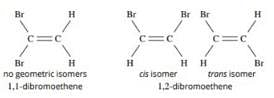
Choose the correct statement(s) regarding isomers of C2H2C12.
Dibromo derivative of a hydrocarbon has molar mass of 200 g (Br = 80) and none of the isomers have any ring structure. Which is/are the correct deduction regarding isomers?
Which of the following carbonyls have four enol isomers?
Pick up the correct statements regarding isomers of C2FCIBrt
Enol isomer of which of the following forms six membered stable ring through intramolecular H-bonding?
Which is/are true regarding pair of geometrical isomers?
Which of the following compounds have more than one pairs of stereoisomers?
A hydrocarbon X (M = 140 g/mol) on catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H22 (Y). Y on chlorination gives only two positional isomers with molecular formula C10H21C1. Which is/are correct about X and Y?
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q.
Match the quantity from Column I with the types of isomerism from Column II
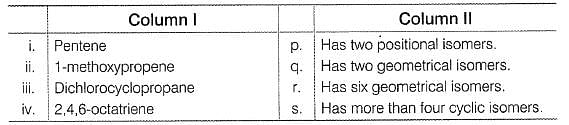
Codes

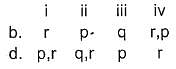
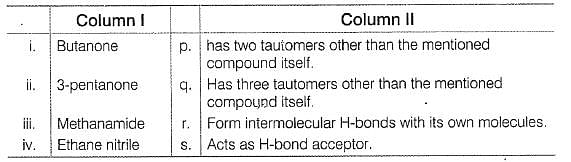
Match the systems in Column I with their corresponding characterstics from Column II
Codes

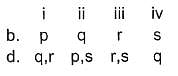
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-26) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
A number of unsaturated hydrocarbons have the same molecular formula C11H22. All of these hydrocarbons on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3,4,6-trimethyloctane.
Q.
How many structural isomers of the starting hydrocarbon, on catalytic hydrogenation can give the mentioned alkane?
Passage I
A number of unsaturated hydrocarbons have the same molecular formula C11H22. All of these hydrocarbons on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3,4,6-trimethyloctane.
Q.
How many of the above unsaturated hydrocarbons are capable of exhibiting geometrical isomerism?
Passage I
A number of unsaturated hydrocarbons have the same molecular formula C11H22. All of these hydrocarbons on catalytic hydrogenation gives the same 3,4,6-trimethyloctane.
Q.
If the product alkane is 3,6-dimethyloctane, how many different isomers. (structural plus geometrical only) of alkenes can give this product?
Passage II
Consider the dollowing molecules to answer the next three questions.
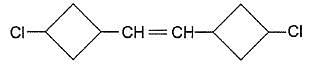
Q.
How many stereoisomers exist for this molecule ?
Passage II
Consier the following molecules to answer the next three questions.
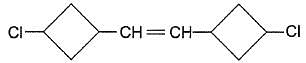
Q.
Treatment of halogenated hydrocarbon with NaBH4 reduces secondary and tertiary halides but olefinic bonds are not affected. If the above mentioned compound is reduced with NaBH4, how many different isomers would be produced?
Passage II
Consider the following molecules to answer the next three questions.
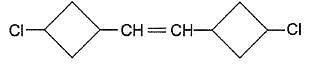
Q.
If the given compound is carefully reduced so that only double bond is reduced, leaving halide bonds intact, how many different stereoisomers would be produced?
Direction (Q. Nos. 27-30) This section contains 4 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
For hydrocarbon with molecular formula C5H8, how many acyclic isomers without consecutive pi-bonds are possible?
How many different isomers of alkene with molecular formula C7H14, on catalytic hydrogenation, can give 3-methyl hexane?
How many geometrical isomers exist in 1,2,4-trichlorocyclopentane?
How many geometrical isomers exist for 1-bromo-2-chloro-3-fluorocyclopropane?
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|


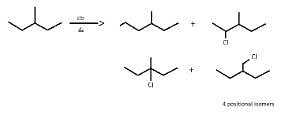 So, X can be
So, X can be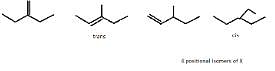
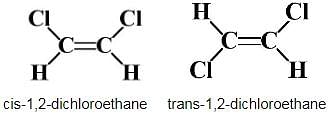 Net dipole moment=0
Net dipole moment=0