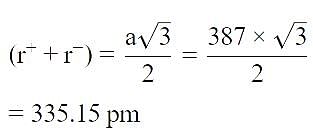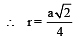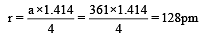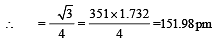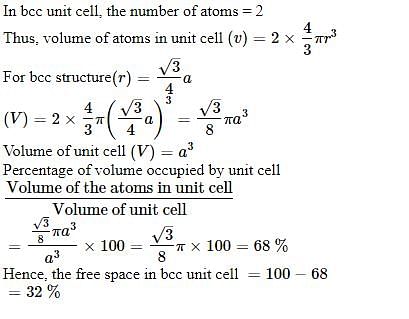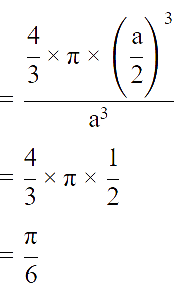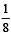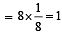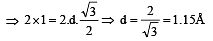31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: The Solid State (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: The Solid State (Old NCERT)
Right option for the number of tetrahedral and octahedral voids in hexagonal primitive unit cell are: [2021]
The number of carbon atoms per unit cell of diamond unit cell is : [NEET 2013]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A metal has a fcc lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g cm-3.The molar mass of the metal is?
(NA Avogadro's constant= 6.02 x 1023 mol-1) [NEET 2013]
Structure of a mixed oxide is cubic close-packed (c.c.p). The cubic unit cell of mixed oxide is composed of oxide ions. One fourth of the tetrahedral voids are occupied by divalent metal A and the octahedral voids are occupied by a monovalent metal B. The formula of the oxide is : [2012 M]
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present in a cubic close-packed structure is : [2012]
A metal crystallizes with a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 408 pm.The diameter of the metal atom is : [2012]
A solid compound XY has NaCl structure. If the radius of the cation is 100 pm, the radius of the anion (Y–) will be : [2011 M]
Among the following which one has the highest cation to anion size ratio? [2010]
AB; crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice with edge length ‘ ’ equal to 387 pm . The distance between two oppositely charged ions in the lattice is : [2010]
Copper crystallises in a face-centred cubic lattice with a unit cell length of 361 pm. What is the radius of copper atom in pm? [2009]
Lithium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic crystal. If the length of the side of the unit cell of lithium is 351 pm, the atomic radius of the lithium will be:[2009]
With which one of the following elements silicon should be doped so as to give p-type of semiconductor ? [2008]
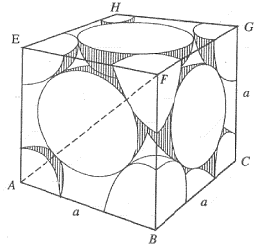
Percentage of free space in a body centred cubic unit cell is : [2008]
The fraction of total volume occupied by the atoms present in a simple cube is
[2007]
Which of the folloiwng anions is present in the chain structure of silicates? [2007]
If NaCl is doped with 10– 4 mol % of SrCl2, the concentration of cation vacancies will be (NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1) [2007]
CsBr crystallises in a body centered cubic lattice.The unit cell length is 436.6 pm. Given that the atomic mass of Cs = 133 and that of Br = 80 amu and Avogadro number being 6.02 × 1023 mol–1, the density of CsBr is
[2006]
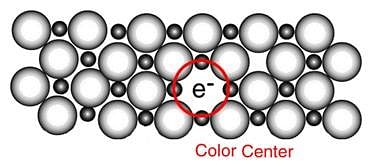
The appearance of colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to [2006]
In face-centred cubic lattice, a unit cell is shared equally by how many unit cells? [2005]
A compound for med by elemen ts X an d Y crystallizes in a cubic structure in which the X atoms are at the corners of a cube and the Y atoms are at the face centres. The formula of the compound is [2004]
When molten zinc is converted into solid state, it acquires HCP structure. The number of nearest neighbours will be [2001]
A compound is formed by elements A and B. The crystalline cubic structure has the A atoms at the corners of the cube and B atoms at the body centre. The simplest formula of the compound is [2000]
The second order Bragg diffraction of X-rays with = 1.00 Å from a set of parallel planes in a metal occurs at an angle 60º. The distance between the scattering planes in the crystal is [1998]
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when [1998]
For two ionic solids CaO and KI, identify the wrong statement amongst the following : [1997]
A solid with high electrical and thermal conductivity from the following is [1994]
When electrons are trapped into the crystal in anion vacancy, the defect is known as : [1994]
The pure crystalline substance on being heated gradually first forms a turbid liquid at constant temperature and still at higher temperature turbidity completely disappears. The behaviour is a characteristic of substance forming [1993]
In graphite electrons are : [1993]
On doping Ge metal with a little of In or Ga, one gets[1993]
|
100 videos|282 docs|123 tests
|


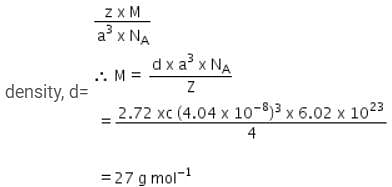
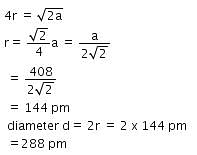
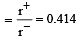
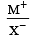 is highest in CsF
is highest in CsF