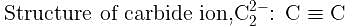Test: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - 1
In which of the following species the underlined carbon is having sp3 − hybridization
Among the following, the species having the smallest bond length is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Among the following the maximum covalent character is shown by which compound:
The hybridisation of orbitals of N atom in NO3–, NO2+, NH4+ are respectively:
Which of the following statements are not correct?
When a gas phase atom in its ground state gains an electron. This is called:
Elements in which apart from 3s and 3p orbitals, 3d orbitals also available for bonding In a number of compounds of these elements there are more than eight valence electrons around the central atom. One such example is:
The number of types of bonds between two carbon atoms in calcium carbide is:
The electronic configuration of the outer most shell of the most electronegative element is:
Rank the bonds in the set C=O, C-O, C≡O, in the order of decreasing bond length:
A qualitative measure of the stability of an ionic compound is provided:
The shift in electron density is symbolized by the crossed arrow in the below diagram. It depicts:
Which one of the following is paramagnetic?
Using MO theory predicts which of the following species has the shortest bond length?
Rank the bonds in the set C=O, C-O, C≡O in order of decreasing bond strength:
Bond lengths are lower in elements having:
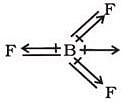
In BF3, the molecule below the dipole moment is zero although the B-F bonds are oriented at an angle of 1200 to one another. Net dipole moment in BF3 molecule is:
Hybridization of C2 and C3 of H3C − CH = C = CH − CH3 are:
Which one of the following pairs of species has the same bond order?
Quartz is very hard and melts at 1550∘C . Reason is:
The shape of the below molecule is:
The sp3d2 hybridization of central atom of a molecule would lead to
Rank the following bonds in order of increasing polarity: H-N, H-O, H-C.
|
129 videos|233 docs|88 tests
|