Test: Covalent Bonding - NEET MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Covalent Bonding
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-16) This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Octet rule is not followed in
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
The correct order of increasing bond length of
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
IV. C=C
In which of the following cases, covalent bonds are cleaved?
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
The bond between two identical nonmetal atoms has a pair of electrons:
Hyperconjugation involve overlap of the following orbitals
Malleability and ductility of metals can be accounted due to
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q.
Match the orbital overlap figures shown in Column I with the description given in Column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns.
[JEE Advanced 2014]
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-19) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE Then ONE is correct.
Peroxide ion ______.
a) is diamagnetic.
b) has five completely filled antibonding molecular orbitals.
c) is isoelectronic with neon.
d) has bond order one.
Which one of these is correct?
Select the correct statement(s) about divalent anion of orthophosphoric acid.
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|



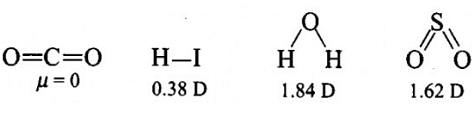
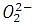 is diamagnetic. Peroxide ion is isoelectronic with argon, not with neon.
is diamagnetic. Peroxide ion is isoelectronic with argon, not with neon. 














