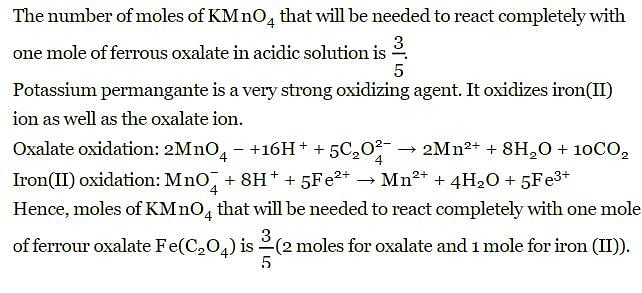Test: Equivalent in Terms of Redox Reactions - NEET MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Equivalent in Terms of Redox Reactions
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. As2S3 (yellow precipitate) is soluble in cone. HNO3 as given in unbalanced equation
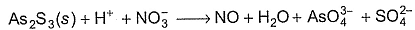
Equivalent weight in terms of molar mass M of As2S3 is
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
In the following reaction, 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) → 3S(S) + 2H2O (l) One equivalent of H2S (g)will reduce
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which has maximum number of equivalents per mole of the oxidant?
Equivalent weight of H3PO2 in a reaction is found to be half of its molecular weight. It can be due to its
KMnO4 (purple) is reduced to K2MnO4 (green) by in basic medium. 1 mole of KMnO4 is reduced by
Equivalent weight of K2Cr2O7 in the following reaction is
(M = molar mass of K2Cr2O7)
In the following disproportionation of Cl2 in basic medium Cl2 + 2KOH → KCl + KClO + H2O equivalent mass of Cl2 is
One mole of CaOCI2 is dissolved in water and excess of Kl added. Hypo (Na2S2O3) required to react oxidised part completely is
Consider conversion of MnCI2 into
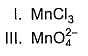
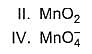
Increasing order of equivalent weights of MnCI2 in these conversions is
The equivalent weight of MnSO4 is half of its molecular weight when it converts to
The number of moles of KMnO4 that will be needed to react with one mole of ferrous oxalate Fe(C2O4) in acidic solution is
The number of moles of K2Cr2O7 that will be needed to react completely with one mole of ferric sulphite in acidic medium is
Photosynthesis of carbohydrates in plants takes place as
6CO2 +12H2O  C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Equivalent weight of CO2 and C6H12O6 respectively are
Equivalent weight of C6H5CHO is equal to molar mass in the following reaction.
Thus, species {A) is
Equivalent w eight of KMnO4 and its reduced species in different mediums are given
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Sulphate (IV) ion reduces chromate (VI) to green coloured salt. Thus,
In which of the following reactions, equivalent mass of the underlined is equal to molar mass?
NaHC2O4 is neutralised by NaOH and can also be oxidised by KMnO4 (in acidic medium). Equivalent weight is related to m olecular w eight (M) of NaHC2O4 in these two reactions as
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-20) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Current fuel cells use the reaction of H2(g) and O2(g) to form H2O (/). Often the H2(g)is obtained by steam reforming of a hydrocarbon, such as
A future possibility is a fuel cell that converts a hydrocarbon such as propane directly to CO2(g) and H2O (/)
Q. Difference in equivalent weights of C3H8 based on I and II is
Current fuel cells use the reaction of H2(g) and O2(g) to form H2O (/). Often the H2(g)is obtained by steam reforming of a hydrocarbon, such as
A future possibility is a fuel cell that converts a hydrocarbon such as propane directly to CO2(g) and H2O (/)
Q. Select the correct statements about reaction II taking place in acidic medium.
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the reactions of H3PO3 (m olar mass = M)in Column I with the corresponding equivalent mass of H3PO3 in Column II
Direction (Q. Nos. 22 and 23) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. How many moles of are formed per mole of Mn2+ reacted in the following reaction?
In certain laboratory process, it is necessary to remove ions from solution by heating with HNO3. Calculate the moles of HNO3 required by 1 mole of (NH4)2SO4
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|