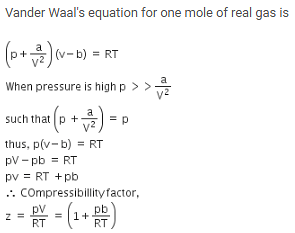Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- States of Matter - JEE MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- States of Matter
According to the kinetic theory of gases, in an ideal gas, between two successive collisions a gas molecule travels –
[AIEEE-2003]
As the temperature is raised from 20°C to 40°C, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following ?
[AIEEE-2004]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In van der Waals equation of state of the gas law, the constant `b' is a measure of -
[AIEEE-2004]
Which one of the following statements is NOT true about the effect of an increase in temperature on the distribution of molecular speeds in a gas ?
[AIEEE-2005]
Equal masses of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at 25ºC. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is –
[AIEEE-2007]
The no. of moles per litre in the equation PV = nRT is expressed by -
[AIEEE-2002]
The correct value of R is -
[AIEEE-2002]
If 10-4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ?
(Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 is 3170 pa; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol)
[AIEEE -2010]
`a' and `b' are Vander Waals' constant for gases. Chlorine is more easily liquefied than ethane because :
[AIEEE - 2011]
When r, P and M represent rate of diffusion, pressure and molecular mass, respectively, then the ratio of the rates of diffusion (rA/rB) of two gases A and B, is given as -
[AIEEE - 2011]
The molecular velocity of any gas is -
[AIEEE - 2011]
The compressibility factor for a real gas at high pressure is –
[AIEEE-2012]
For gaseous state, if most probable speed is denoted by C*, average speed by and mean square speed by C, then for a large number of molecules the ratios of these speeds are :
[Jee(Main) 2013, 3/120]
A gaseous hydrocarbon gives upon combustion 0.72 g of water and 3.08 g. of CO2. The empirical formula of the Hydrocarbon is :
[Jee(Main) 2013, 3/120]
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|