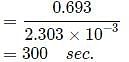R.C. Mukherjee Test: Chemical Kinetics - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - R.C. Mukherjee Test: Chemical Kinetics
The rate of a reaction is expressed in different ways as follows :
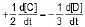 =
= 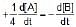
The reaction is :
The rate constant for the forward reaction A(g) 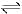 2B(g) is 1.5 × 10-3 s-1 at 100 K. If 10-5 moles of A and 100 moles of B are present in a 10 litre vessel at equilibrium then rate constant for the backward reaction at this temperature is
2B(g) is 1.5 × 10-3 s-1 at 100 K. If 10-5 moles of A and 100 moles of B are present in a 10 litre vessel at equilibrium then rate constant for the backward reaction at this temperature is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Reaction A + B → C + D follow's following rate law : rate = k[A]+1/2[B]1/2. Starting with initial conc. of 1 M of A and B each, what is the time taken for concentration of A of become 0.25 M.
Given : k = 2.303 × 10-3 sec-1.
Consider the following first order competing reactions :
X 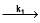 A+ B and y
A+ B and y 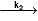 C+D
C+D
if 50% of the reaction of X was completed when 96% of the reaction of Y was completed, the ratio of their rate constants is
Units of rate constant for first and zero order reactions in terms of molarity (M) are respectively.
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about
For a reaction pA + qB → products, the rate law expression is r = k[A]l[B]m, then :
In the reaction : A + 2B → 3C + D, which of the following expression does not describe changes in the conc. of various species as a function of time :
A first order reaction is 87.5% complete in an hour. The rate constant of the reaction is
Half-life period of a second order reaction is
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 20 minutes at 27°C and in 5 min at 47°C. The energy of activation of the reaction is
For the first order reaction A → B + C, carried out at 27°C if 3.8 × 10-16% of the reactant molecules exists in the activated state, the Ea (activation energy) of the reaction is
The rate constant, the activation energy and the Arrhenius parameter (A) of a chemical reaction at 25°C are 3.0 × 10-4 s-1, 104.4 kJ mol-1 and 6.0 × 10-4s-1respectively. The value of the rate constant at T → ∞ is
The following mechanism has been proposed for the exothermic catalyzed complex reaction.
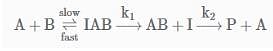
If k1 is much smaller than k2. The most suitable qualitative plot of potential energy (P.E.) versus reaction coordinate for the above reaction.
The activation energy of a reaction at a given temperature is found to be 2.303 RT J mol–1. The ratio of rate constant to the Arrhenius factor is
Consider 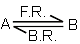 + heat, If activation energy for forward reaction is 100 kJ/mole then activation energy for backward reaction and heat of reaction is :
+ heat, If activation energy for forward reaction is 100 kJ/mole then activation energy for backward reaction and heat of reaction is :
In a reaction, the thershold energy is equal to :
The first order rate constant k is related to temperature as log k = 15.0 - (106/T). Which of the following pair of value is correct ?
When a graph between log K and 1/T is drawn a straight line is obtained. The temperature at which line cuts y-axis and x-axis.
The rate constant, the activation energy and the frequency factor of a chemical reaction at 25°C are 3.0 × 10-2 s-1, 104.4 KJ mol-1 and 6.0 × 1014 s-1 respectively. The value of the rate constant as T → ∞ is :
The rate data for the net reaction at 25°C for the reaction X + 2Y → 3Z are given below :
[X0] [Y0] Time required for [Z] to increase by 0.005 mol per litre.
0.01 0.01 72 sec
0.02 0.005 36 sec
0.02 0.01 18 sec
The intial rate (as given by Z) is :
The rate of production of NH3 in N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 is 3.4 kg min-1. The rate of consumption of H2 is :
For a given reaction of first order it takes 20 min. for the conc. to drop from 1.0 M to 0.60 M. The time required for the conc. to drop from 0.60 M to 0.36 M will be :
For a first order reaction, the concentration of reactant :
Radioactivity of a sample (z = 22) decreases 90% after 10 years. What will be the half-life of the sample?
Mathematical representation for t1/4 life for first order reaction is over is given by :
For a reaction A → Products, the conc. of reactant C0, aC0, a2C0, a3C0............ after time interval 0, t, 2t ............ where 'a' is constant. Then :
Half-life is independent of conc. of A. After 10 minutes volume N2 gas is 10 L and after complete reaction 50 L. Hence rate constant in min-1 :
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
In acidic medium the rate of reaction between (BrO3)- & Br- ions is given by the expression, –[d(BrO3-) /dt] = K[BrO3-][Br-][H +]2 It means :
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|