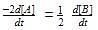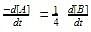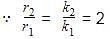Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Chemical Kinetics - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Chemical Kinetics
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
A chemical reaction [2A] + [2B] + [C] → product follows the rate equation :  then order of reaction is - [AIEEE-2002]
then order of reaction is - [AIEEE-2002]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The unit of rate constant of first & second order reaction is respectively -
In the equation Kt = log C0 – log Ct, the curve between t and log Ct is -
[AIEEE-2002]
Consider following two reactions
Units of k1 and k2 are expressed in terms of molarity (mol L–1) and time (sec–1) as –
[AIEEE-2002]
H2 gas is adsorbed on the metal surface like tungsten. This follows........ order reaction –
[AIEEE-2002]
In respect of the equation k = Ae –Ea/RT in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is
correct?
[AIEEE-2003]
For the reaction system: 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order with respect to O2 and second order with repect to NO, the rate of reaction will –
[AIEEE-2003]
The rate law for a reaction between substances A and B is given by
Rate = k [A]n [B]m
On doubling the concentration of A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of the reaction will be as–
[AIEEE-2003]
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant, decreases from 0.8 M to 0.4 M in 15 minutes. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M is -
[AIEEE-2004]
The rate equation for the reaction 2 A + B → C is found to be : rate = k [A] [B] . The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
[AIEEE-2004]
Consider an endothermic reaction X → Y with the activation energies Eb and Ef for the backward and forward reactions, respectively. In general
[AIEEE-2005]
A reaction involving two different reactants can never be –
[AIEEE-2005]
t1/4 can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 3/4 of its initial value. If the rate constant for a first order reaction is K, t1/4 can be written as –
[AIEEE-2005]
A reaction was found to be second order with respect to the concentration of carbon monoxide. If the concentration of carbon monoxide is doubled, with everything else kept the same, the rate of reaction will -
[AIEEE 2006]
Rate of reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation as k = Ae–E/RT , In this equation, E represents
[AIEEE 2006]
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO with Br2 to form NOBr :
NO(g) + Br2 (g) NOBr2 (g)
NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) → 2 NOBr (g)
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to NO (g) is -
[AIEEE 2006]
The energies of activation for forward and reverse reactions for A2 + B2 2AB are 180 kJ mol–1 and 200 kJ mol–1 respectively. The presence of a catalyst lowers the activation energy of both (forward and reverse) reactions by 100 kJ mol–1. The enthalpy change of the reaction (A2 + B2 → 2AB) in the presence of catalyst will be (in kJ mol–1) –
[AIEEE 2007]
Consider the reaction, 2A + B → Products. When concentration of B alone was doubled, the half-life of B did not change. When the concentration of A alone was doubled, the rate increased by two times. The unit of rate constant for this reaction is –
[AIEEE 2007]
For a reaction 1/2 A→ 2B, rate of disappearance of ‘A’ related to the rate of appearance of ‘B’ by the expression -
[AIEEE 2008]
The half life period of a first order chemical reaction is 6.93 minutes. The time required for the completion of 99% of the chemical reaction will be (log 2 = 0.301)
[AIEEE 2009]
The time for half life period of a certain reaction A → products is 1 hour. When the initial concentration of the reactant ‘A’, is 2.0 mol L–1, how much time does it take for its concentration to come from 0.50 to 0.25 mol L–1 if it is a zero order reaction ?
[AIEEE 2010]
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10ºC rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50ºC, the rate of the reaction increases by about :
[AIEEE 2011]
For a first order (A) → Products, the concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 minutes. The rate of reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M, is :
[AIEEE 2012]
The rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Activation energy of such a reaction will be: (R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1 and log 2 = 0.301)
[IIT Mains 2013]



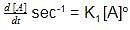
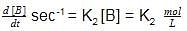
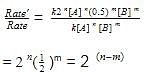

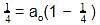
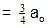
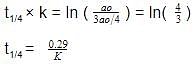
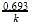
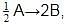 rate of disappearance of A is related to rate of appearance of B by the expression:
rate of disappearance of A is related to rate of appearance of B by the expression: