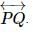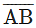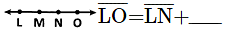Olympiad Test: Basic Geometrical Ideas - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 - Olympiad Test: Basic Geometrical Ideas
What is the simplest of all geometrical figures which has no size but has a position?
What is a set of points which extend infinitely in both directions called?
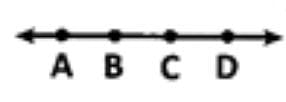
Name the set of points which is a part of a line with two end points.
How do you write a line segment AB symbolically?
What is the symbolic representation of a ray OP?
What is the number of end points of a Straight line?
What is a set of points extending infinitely in all directions on the same flat surface called?
How many lines can be drawn passing through a given point?
How many lines can you draw joining two distinct points in a plane?
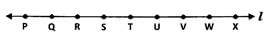
Three points P, Q and R are said to be collinear. Where do they lie?
Four lines p, q, r and s are said to be concurrent. What do they pass through?
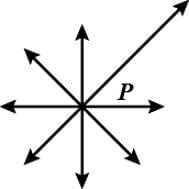
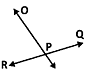
In the given figure what is point P called?
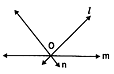
In the given figure, what are lines l, m and n called?
In the given figure, what are points P, O and Q called?
Which instrument is used to compare two line segments?
Which of these instruments is not used to construct a line segment?
|
92 videos|348 docs|54 tests
|