Test: Air, Water And Weather - 2 - Class 5 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 5 - Test: Air, Water And Weather - 2
Ramesh take a glass of water, added a spoonful of sugar and pinch of salt and also squeezed the juice of a lemon into it. After stirring it properly it was filtered with a strainer. What will be left in the strainer?
Which of the following will not dissolve in water?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When we go up in the sky. The atmospheric pressure will
The figure shows a straw placed in a glass of lassi. The level of lassi in the straw rises when air is sucked out. This is because

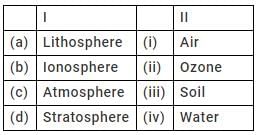
Atmosphere is the part of earth which consists of
Regarding air, which of the following statement(s) is / are true
(i) Air has no mass
(ii) Air is needed for burning
(iii) Air exerts pressure from all sides and on everything
Which of the following process is component of water cycle?
Air exerts pressure can be shown by which of the following example?
Which of the following picture correctly represents the composition of air? Where P = Nitrogen, Q = Oxygen, R = Inert gas, S = Carbon dioxide
When we flipa glass full of water with a cardboard beneath it, the water doesn't spills out because
When we put a block of wood in fresh water it floats on it. What will happen if the same block is dropped in water from ocean (Saline) water?
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|