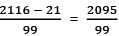CAT Exam > CAT Tests > Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) > Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - CAT MCQ
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - CAT MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 for CAT 2024 is part of Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) preparation. The Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the CAT exam syllabus.The Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 MCQs are made for CAT 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 below.
Solutions of Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 questions in English are available as part of our Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) for CAT & Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 solutions in
Hindi for Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for CAT Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 | 15 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for CAT preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) for CAT Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 1
What is the Place Value and Face Value of 7 in 78654?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 1
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 2
The difference between place value of two 9’s in 49891 is
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 3
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 4
Which of the following is a Real Number but not a Rational Number?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 5
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 6
√16 will not fall under which of the following categories?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 6
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 7
(16a + 6) will fall under which of the following categories, a is an Integer
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 7
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 8
If (7a - 3) is odd then 'a' would be, a is an Integer
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 8
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 9
What is the smallest possible positive Integer?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 12
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 13
What is the difference between 517th Whole number and 516th Natural Number?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 14
Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 15
How many pairs of consecutive prime numbers are there?
Detailed Solution for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 - Question 15
|
191 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
Information about Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Arun Sharma Test: Number System- 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
191 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
Download as PDF


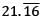 in p/q form
in p/q form