Economics: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 2
Budget is a statement of actual annual receipts and expenditures of the government.
Central Budget is presented in India on ______every year by the Finance Minister.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In India _______ type of taxes are generally of no or little significance due to their very low revenue yield to government?
Production of goods which are socially harmful are discouraged by..............
Surplus budget is when actual receipts exceeds estimated expenditures.
In 2017 government of India brought an important reform in the tax system of the country by introducing GST.
Which of the following type of tax is GST?
Rahul dies without a legal heir. His property stands transferred to the government. The income under this head will be referred to as ‘Special assessment’.
_______ deficit includes interest payment by the government on the past loans.
Primary deficit in a government budget will b e zero, when _______
Budget deficit is equal to total expenditure minus total receipts.
Which of the following measures of meeting deficit in budget, leads to an increase in money supply in the economy?
If borrowings and other liabilities are reduced to the budget deficit, we get
If primary deficit is ₹ 3,000 and interest payment is ₹ 500, the fiscal deficit is
From the given information, calculate: Fiscal Deficit
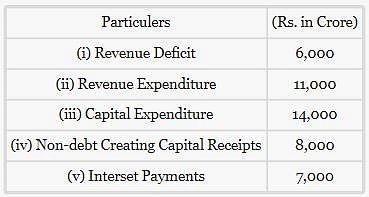
_______ deficit includes interest payment by the government on the past loans.
Economic stability and equitable distribution of income and wealth can be achieved by the budgetary policy of the government.
_______ is not an example of non-tax revenue from below.
Developing countries generally prepares a balanced budget.
Recently the union government introduced TJjjawala Yojna, which provides free LPG commission to the women in rural area. Which of the following objective of government budget is fulfilled in this case?
SEZ are created by the government to achieve the objective of
|
8 docs|148 tests
|

















